丝膜菌属Cortinarius (Pers.) Gray隶属于担子菌门Basidiomycota、蘑菇纲Agaricomycetes、蘑菇目Agaricales、丝膜菌科Cortinariaceae,该属是蘑菇目中最大的属,目前已描述的物种超过2 000种,分布全球(Niskanen et al. 2016),在我国,2018年编制的《中国生物多样性红色名录-大型真菌卷》记录了丝膜菌属物种200种,分布于我国大部分地区。丝膜菌属真菌具有重要的生态价值和经济价值,一方面,该属真菌可以与一些乔木、灌木形成外生菌根,在植物生长和森林生态系统中发挥着重要作用(Bödeker et al. 2014;Defrenne et al. 2019);另一方面,丝膜菌属的一些种类具有食药用价值。此外,还有一些种类含有奥来毒素(orellanine),是剧毒的,会导致急性肾衰和死亡;近年研究表明,丝膜菌的奥来毒素可用于肾小管上皮转移性肾癌的治疗,可望开发成治疗药物(Buvall et al. 2017)。
自Grzymala(1957)首次记载波兰科宁省102例奥来丝膜菌Cortinarius orellanus引起中毒事件以来,由丝膜菌属物种引起的中毒事件在欧洲大陆、北美、亚洲和澳大利亚都有报道。60余年来,各国科学家对有毒丝膜菌的方方面面开展了大量研究工作,本文对丝膜菌属有毒蘑菇中毒及种类、中毒症状、毒素成分与检测、毒性毒理和中毒治疗以及毒素应用等方面进行总结,进而对一些研究热点进行展望。
1 丝膜菌引起的中毒事件及其种类
1952年,在波兰科宁省发生了一起102人蘑菇中毒11人死亡的事件,中毒症状最主要特征表现为潜伏期长(3-14d)和肾损伤,波兰医生Grzymala(1957)首次对其进行了报道。Skirgiello & Nespiak(1957)鉴定出引起中毒的物种为奥来丝膜菌Cortinarius orellanus。之后,1958-1965年在波兰又陆续报道了一些中毒事件,这期间共发生144例中毒,其中25人死亡(Schumacher & Hoiland 1983)。Moser(1971)报道了德国一起2人误食C. speciosissimus引起的急性肾损害中毒事件,之后的10年内,在欧洲的瑞士、法国、芬兰、瑞典、苏格兰和挪威等国家,由这2个种引起的中毒事件有180多例(Schumacher & Hoiland 1983);Gerault(1981)报道在法国由C. splendens引起的中毒事件,其中毒症状与C. orellanus和C. speciosissimus相同。Danel et al.(2001)综述了欧洲11个国家1965-1999年报道的245例中毒事件,导致中毒的物种有C. orellanus、C. rubellus(与C. speciosissimus同物异名)、C. splendens、C. cinnamomeus以及该属的其他物种(Cortinarius spp.),其中最主要的是C. orellanus、C. rubellus和C. splendens,占94.5%。Bouhbouh et al.(2011)报道了荷兰一例由丝膜菌C. cinnamomeus引起肾衰的中毒事件。近年来,在欧洲,由以上丝膜菌引起的中毒事件时有记载(Esposito et al. 2015;Hedman et al. 2017)。
除欧洲外,在北美也有由丝膜菌引起的中毒事件。Raff et al.(1992)报道了一起由丝膜菌引起肾损害的事件,并认为是北美首例。之后,Judge et al.(2010)报道了密西根1例中毒事件,经ITS序列和分子系统发育分析,表明该有毒丝膜菌是个新种,命名为C. orellanosus。此外,在澳大利亚也有3例疑似由丝膜菌引起的肾损害中毒事件(Mount et al. 2002)。
在我国,早年记载陕西发生过误食丝膜菌中毒和死亡的事件,但是没有确定具体是哪个种(卯晓岚 2006)。由于丝膜菌中毒潜伏期长为3-14d,中毒患者发病时不会想到是由几天前吃野生蘑菇所引起,导致中毒原因难以确定,给中毒调查及物种确定带来了很大困难,因此,在我国一些误食丝膜菌中毒的事件很少得到追踪和调查。
2 丝膜菌奥来毒素的检测方法和含奥来毒素的种类
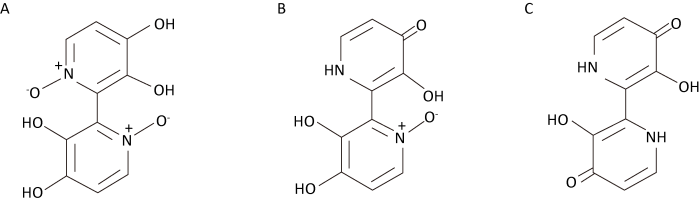
Grzymala(1962)最早从Cortinarius orellanus分离出一种有毒物质,称之为奥来毒素(orellanine),这种物质对动物产生的毒性作用与蘑菇子实体对动物产生的毒性作用相同。之后,Antkowiak & Gessner(1979,1985)首先从C. orellanus和C. speciossimus中分离纯化出奥来毒素,完成了该毒素的化学结构鉴定,认为奥来毒素加热到270℃以上或者经光照会产生化学分解,先产生同样具有毒性的orellinine,最后形成一种叫orelline的无毒性的化合物。Orellanine、orellinine和orelline的化学结构见图1。
Dehmlow & Schultz(1985)人工合成了orellanine和orelline,之后Cohen-Addad et al.(1987)用X-射线晶体衍射证实了Antkowiak & Gessner(1985)提出的结构。奥来毒素在蘑菇体内稳定,烹煮、冷冻或者干燥不会破坏奥来毒素,甚至经20年贮藏后,都不会被破坏(Dinis-Oliveira et al. 2016)。
鉴定一种蘑菇是否有毒,除了通过中毒事件直接确定外,如果该类毒蘑菇的毒素成分已知,还可以通过毒素成分检测来确定。因此,在丝膜菌的毒素成分确定后,一些研究者通过检测丝膜菌属物种的毒素成分来确定物种的毒性。主要的方法包括:(1)薄层层析色谱(TLC)法:早期主要是利用TLC方法,Keller-Dilitz et al.(1985)利用TLC法分析了5种丝膜菌的14份样本,结果表明C. orellanoides、C. orellanus、C. rainierensis 和C. speciosissimus含有奥来毒素,而C. fluorescens没有检测出。Rapior et al.(1988)利用TLC方法检测了丝膜菌属和Dermocybe属(该属现已归为丝膜菌属)中一些物种的奥来毒素,结果表明丝膜菌属Leprocybe亚属Orellani组的8个物种中有7种都含有奥来毒素,它们分别为C. brunneofulvus、C. fluorescens、C. henrici、C. orellanoides、C. orellanus、C. rainierensis和C. speciosissimus,而该组中的C. fulvaureus不含奥来毒素,故认为该种不应该放在该组中。同时,丝膜菌属Cortinarius亚属、Phlegmacium亚属和Leprocybe亚属中其他组的28种丝膜菌以及Dermocybe 属的13个种都没有检测出奥来毒素。Oubrahim et al.(1997)利用3种不同方法(TLC法、电泳法和电子自旋共振法)检测了34种丝膜菌科物种的奥来毒素,表明只在丝膜菌属Leprocybe亚属Orellani 组中的5种丝膜菌,即C. henrici、C. orellanoides、C. orellanus、C. rainierensis和C. speciosissimus含有奥来毒素。
图1
图1
Orellanine(A)、orellinine(B)和orelline(C)的化学结构式(引自Antkowiak & Gessner 1985)
Fig. 1
Structures of orellanine (A), orellinine (B), orelline (C) (cited from Antkowiak & Gessner 1985).
(2)高效液相色谱(HPLC)法:自上世纪80年代末至90年代起,随着HPLC的广泛应用,研究者利用HPLC结合不同检测方法如电化学(Holmdahl et al. 1987)、光电二极管(Koller et al. 2002)和紫外光(Shao et al. 2016)分别建立了丝膜菌毒素的分离和检测方法,极大地提高了检测灵敏度。Koller et al.(2002)利用HPLC分别检测了丝膜菌C. orellanus 和C. rubellus子实体菌盖、菌柄、孢子以及菌根中的奥来毒素含量;Shao et al.(2016)利用HPLC检测出北美的一种丝膜菌C. armillatus中含有奥来毒素,其毒素含量达到145μg/g,其检测极限可达到17μg/g。(3)液相色谱-质谱(HPLC-MS)法:这是近年来新发展起来的检测丝膜菌毒素的快捷灵敏方法。Herrmann et al.(2012)利用HPLC-ESI-MS/MS分析了C. rubellus子实体中的奥来毒素,表明检测极限达到4.9ng/mL;Anantharam et al.(2016)建立了利用HPLC和LC-MS/MS检测肾组织中奥来毒素的方法,研究表明HPLC检测极限为10μg/g,而LC-MS/MS可达20ng/g;在开展奥来毒素在小鼠体内的代谢动力学研究时,Najar et al.(2018)采用了LC-MS/MS检测跟踪奥来毒素在小鼠血浆中的变化情况。Shao et al.(2016)利用HPLC和LC-MS/MS检测出北美的蜜环丝膜菌C. armillatus中含有奥来毒素,其毒素含量达到145μg/g,因此认为该种是一种新的含奥来毒素的蘑菇。以前认为有毒的含奥来毒素的丝膜菌都在Leprocybe亚属Orellani组(Shao et al. 2016),然而分子证据表明C. armillatus属于Telamonia亚属Armillati组(Niskanen et al. 2011)。由于以前的奥来毒素检测都是基于灵敏度不高的TLC法,并且对于物种的分类鉴定是采用传统的形态分类方法,因此,随着高灵敏度检测方法的建立以及分子标记用于物种鉴定,相信会有更多的丝膜菌属物种检测出奥来毒素。
综上所述,通过丝膜菌中毒事件和丝膜菌中奥来毒素的检测,到目前已知的丝膜菌属有毒物种包括有:Cortinarius armillatus (Fr.) Fr.、C. brunneofulvus Fr.、C. cinnamomeus (L.) Gray、C. fluorescens E. Horak、C. henrici Reumaux、C. orellanus Fr.、C. orellanosus Ammirati & Matheny、C. splendens Rob. Henry、C. rainierensis A.H. Sm. & D.E. Stuntz、C. rubellus Cooke(与C. orellanoides、C. speciosissimus同物异名)等。
3 丝膜菌中毒的临床症状
Grzymala(1957)最早对丝膜菌中毒后的临床症状进行了描述,认为是一种新的蘑菇中毒症状。之后在欧洲报道了大量的由丝膜菌属物种Cortinarius orellanus和C. speciosissimus引起的中毒案例及其临床症状表现,Danel et al.(2001)收集了245例中毒案例,并对其中有详细记录的90例进行了临床症状特征综合分析。
丝膜菌中毒后的临床症状表现按中毒进展过程可分为4个阶段:潜伏期、肾损前期(或胃肠期)、肾损害期和恢复期(Spoerke & Rumack 1994;Danel et al. 2001;Dinis-Oliveira et al. 2016)。(1)潜伏期,为食用后36h到17d,平均为3d。潜伏期的长短与中毒的程度有关,潜伏期越短中毒越严重。轻微中毒者,潜伏期10-17d,症状表现为口干舌燥、口渴、多尿,几天后恢复正常;中等程度中毒者,潜伏期是6-10d,症状表现为消化障碍、多尿或少尿、血尿和白细胞增多,但没有严重的肾功能障碍,3到4周可恢复正常;严重中毒者,潜伏期2-3d,症状表现为急性肾衰竭,死亡率高达50%(Dinis-Oliveira et al. 2016);(2)肾损前期,肠胃、神经和一般症状通常持续1周,症状表现为呕吐、恶心、腹泻、厌食、突然发冷、打寒颤、发抖、嗜睡、眩晕、味觉障碍和感觉异常;(3)肾损害期,主要出现少尿、白细胞增多、血尿、蛋白尿、无尿、葡萄糖尿、血清中的肌酐、钾、尿素升高、肾组织病理学分析提示肾小管间质性肾炎、间质水肿、炎性浸润、纤维化/硬化;(4)恢复或后遗症期,康复很慢,一般需几个星期或几个月。在瑞典治疗的22例患者中有9例(41%)出现慢性肾功能衰竭,需要间歇透析或肾移植(Holmdahl & Blohmé 1995)。
4 奥来毒素的毒性毒理与中毒治疗
研究人员利用有毒丝膜菌子实体和奥来毒素进行了大量的动物毒性试验。动物实验研究表明,不同动物、不同给毒方式,其半致死剂量不同(Dinis-Oliveira et al. 2016)。对于小鼠,口喂奥来毒素其半致死量LD50为33-90mg/kg体重;腹腔注射其LD50是12.5-15mg/kg体重,口喂干的毒丝膜菌子实体,其LD50是2.2-3.1g/kg体重;对于猫,口喂奥来毒素其半致死量LD50为8.3mg/kg体重;口喂干的毒丝膜菌子实体,其LD50是0.97g/kg体重;临床数据表明人对奥来毒素似乎比小鼠和大鼠更敏感,仅仅2-3个蘑菇足够产生严重的肾衰(Calvino et al. 1998)。Herrmann et al.(2012)认为,新鲜的有毒丝膜菌C. rubellus对于体重70kg的人来说,其致死量估计是29-227g。
奥来毒素的作用靶标是肾细胞,对肾损伤的机制目前还没有完全弄清楚,关于它的毒理有多种假说:(1)Orellanine强烈抑制大分子如蛋白质、RNA和DNA的合成,很可能是由其代谢产物所导致(Richard et al. 1991;Danel et al. 2001);(2)体外、体内实验表明Orellanine能产生氧自由基,引起过氧化作用,导致肾功能受损害(Oubrahim et al. 1998;Nilsson et al. 2008);(3)Orellanine促进了对碱性磷酸酶、γ-谷氨酰转肽酶和亮氨酸氨基肽酶活性的非竞争性抑制(Ruedl et al. 1989)。
奥来毒素主要作用于肾,主要症状是发生急性肾炎,严重者发展到肾衰竭,如果得不到及时治疗,会引起死亡。对于丝膜菌引起的肾损伤总的治疗原则主要是采用急性肾衰的支持治疗方法,如血液透析、血浆置换和腹膜透析,如果急性肾衰发展为慢性肾衰,则需进行肾移植。
血液透析:在丝膜菌中毒后,有74%的急性肾衰患者采用了血液透析和腹膜透析(Danel et al. 2001)。Bouget et al.(1990)报道了一起 26人误食Cortinarius orellanus中毒事件,其中12人出现急性肾衰症状,8人进行了血液透析,最后8人很快恢复,另外4人发展成慢性肾衰,因此认为血液透析是唯一适合的治疗方法。体外血液灌流、血液透析和血浆置换的作用是从循环中去除毒素,因此认为只有当患者在摄入后1周内时才应考虑(Fulde et al. 1998;Montoli et al. 1999),在此之后,血液透析的使用仅取决于是否需要支持肾功能(Dinis-Oliveira et al. 2016)。
肾移植:奥来毒素中毒严重者易发展为慢性肾衰竭,在经保守治疗无效后通常需要考虑肾移植,因奥来毒素中毒引起慢性肾衰竭而进行了肾移植的病例报道不少,最早Short et al.(1980)报道了2例,2名患者误食了有毒的Cortinarius speciosissimus,直到摄入后10d才到医院就诊,已发展成严重的肾功能衰竭,对其进行了间歇性血液透析,9个月后接受了肾移植。之后因丝膜菌中毒引起慢性肾衰竭而进行了肾移植的报道屡见不鲜(Holmdahl & Blohmé 1995;Duvic et al. 2003;Nagaraja et al. 2015)。肾移植不宜过早,一般在中毒后9-10个月进行,这时不会受到奥来毒素的进一步影响(Dinis-Oliveira et al. 2016)。
药物治疗:对于丝膜菌的中毒治疗,到目前还没有特效解毒药物,但是在动物实验和临床治疗中对一些药物进行了实验和应用。(1)环磷酰胺(cyclophosphamide):在动物实验中,Niemine et al.(1976)通过大鼠实验表明,在口服Cortinarius speciosissimus蘑菇的同时单剂量(150mg/kg)的环磷酰胺可防止肾炎,不过此后没有进一步的实验报道,也没有人类临床使用环酰胺治疗丝膜菌中毒的报道。但是,近年来一些实验和临床表明环磷酰胺在其他原因引起的肾衰治疗中具有良好效果(Cristina et al. 2018;Scolari et al. 2019)。(2)皮质类固醇(corticosteroids):对9位患者在进食毒蘑菇后11-19d用皮质类固醇进行治疗,结果表明肾衰竭没有进一步恶化。之后几例临床治疗也采用了皮质类固醇与其他药物一起治疗,认为早期使用高剂量抗氧化剂治疗和类固醇治疗可能有效地降低了慢性肾功能衰竭的风险(Kilner et al. 1999;Wörnle et al. 2004;Kerschbaum et al. 2012)。(3)N-乙酰半胱氨酸(N-acetylcysteine):由于奥来毒素Orellanine能产生氧自由基,引起过氧化作用,导致肾功能受损害(Oubrahim et al. 1998;Nilsson et al. 2008),N-乙酰半胱氨酸作为谷胱甘肽供体和抗氧化剂,因此有多例丝膜菌中毒的临床治疗中联合使用了N-乙酰半胱氨酸和皮质类固醇(Kilner et al. 1999;Wörnle et al. 2004;Kerschbaum et al. 2012),但是,通过临床病例对比治疗后,Grebe et al.(2013)认为N-乙酰半胱氨酸和皮质类固醇的效果并不理想,不过他们认为从机理上来说这两种药物应该是有效的,可能是他们接收的患者由于潜伏期太长,耽误了治疗时期。
5 奥来毒素在肾癌治疗中的应用
利用有毒蘑菇中的毒素成分治疗癌症一直是科学家追求的研究热点,近10年来,在利用剧毒鹅膏中的鹅膏毒肽(amanitin)与肿瘤免疫靶向治疗和肿瘤药物靶向治疗相结合方面取得了重要进展。陈作红(2014)对2014年之前的研究进展进行了综述,此后利用鹅膏毒肽治疗肿瘤成为了研究热点,并取得了良好进展(Liu et al. 2015a,2015b;Kume et al. 2016;Wyatt et al. 2018;Frischknecht et al. 2019)。
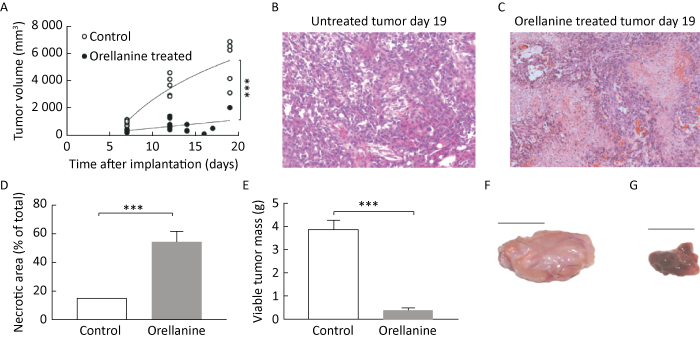
奥来毒素作用靶点为肾细胞,那么是否对肾细胞癌具有毒杀作用呢?为此,瑞典的3个医学研究机构联合开展了研究,2012年他们首次在美国癌症研究协会芝加哥年会上报告了初步研究结果,表明来自丝膜菌的毒素NC-001对肾脏近端肾小管细胞具有特异性毒性,并且这种敏感性也被扩展到从这些肾小管细胞癌变而来的肾癌细胞,分子机理表明丝膜菌毒素通过诱导细胞凋亡导致癌细胞坏死(Hedman et al. 2012)。之后的几年,他们联合了6个医学研究机构,利用化学合成的奥来毒素以大鼠为模型开展了更加深入的肾细胞癌治疗研究,研究结果表明奥来毒素可诱导近端肾小管细胞和所有原代和细胞系肾癌细胞的剂量依赖性死亡,而在对照细胞中没有检测到毒性。奥来毒素的毒性作用包括降低蛋白质合成、破坏细胞代谢和诱导细胞凋亡。在携带人类肾癌异种移植物的裸鼠中,短暂的奥来毒素治疗可消除90%以上的肿瘤。因此,Buvall et al.(2017)认为奥来毒素治疗肾癌具有潜在价值(图2)。
图2
图2
奥来毒素可显著降低肿瘤生长并诱导坏死(引自Buvall et al. 2017)
Fig. 2
Orellanine significantly reduces tumor growth and induces necrosis (cited from Buvall et al. 2017).
6 展望
我国的野生蘑菇资源丰富,人们也喜欢采集食用。由于不能正确区分可食和有毒的种类,误食有毒蘑菇中毒已经成为我国食物中毒事件中导致死亡的最主要因素(周静等 2016)。通过调查发现,我国有毒蘑菇主要包括鹅膏菌属Amanita、环柄菇属Lepiota、盔孢伞属Galerina、裸盖菇属Psilocybe、红菇属Russula、丝盖伞属Inocybe以及牛肝菌科Boletaceae等科属的物种,导致的中毒症状类型可分为7种类型(Chen et al. 2014;陈作红等 2016)。由丝膜菌引起的肾损害型中毒由于其潜伏期长达3-14d,误食中毒后人们很难将中毒与几天前吃的野生蘑菇联系起来,导致中毒原因难以确定,给中毒溯源调查及物种确定带来了很大困难。因此,在我国,尽管早年曾记载陕西发生过误食丝膜菌中毒和死亡事件(卯晓岚 2006),但近年来由丝膜菌引起的中毒事件很少得到调查。
近年来,国际上对于南北半球的丝膜菌属的分子系统发育开展了深入研究,并基于分子证据和形态特征发表了大量新种(Liimatainen et al. 2017,2020;San-Fabian et al. 2018;Pastor et al. 2019;Soop et al. 2019),我国2018年编制的《中国生物多样性红色名录-大型真菌卷》记录了丝膜菌属物种200种,李玉等(2015)编著的《中国大型菌物资源图鉴》记录了丝膜菌属物种30种,Wu et al.(2019)记载了我国丝膜菌属35种。以上记载的绝大部分物种名称都是欧美发表的物种。我国对于丝膜菌属物种的多样性和分类研究还很不够,丝膜菌属物种的分子系统发育研究几乎还处于空白状态。在Wu et al.(2019)记载的35种丝膜菌中,认为可以食用或具药用价值的有26种,具有毒性的15种。图力古尔等(2014)记载了有毒的丝膜菌属物种12种。这些都是依据文献整理的。开展我国丝膜菌属物种多样性及其分子系统发育研究以及有毒物种的确定,十分重要也很有必要。
肾癌是一种广泛的恶性肿瘤,每年报告超过35万例,造成14万人死亡,治疗肾癌尽管有了一些方法,但是对于转移性肿瘤或者晚期肿瘤患者的治疗效果仍然很差(Capitanio & Montorsi 2016)。Buvall et al.(2017)首先报道了丝膜菌中的奥来毒素具有治疗肾癌的作用,开启了奥来毒素治疗肾癌的大门。丝膜菌属于共生菌,不能像腐生菌那样进行人工栽培,因此野生的剧毒丝膜菌资源是有限的,靠从野生的丝膜菌中获取大量毒素资源用于药物研发是不可行的,但是,由于奥来毒素可以通过化学方法合成,并且同样具有毒性(Buvall et al. 2017),这就为奥来毒素开发成治疗肾癌的药物提供了很好的资源。因此,相信在未来一段时间里,开展奥来毒素治疗肾癌及其药物研发会成为一个研究热点。
参考文献
Improved tissue-based analytical test methods for orellanine, a biomarker of Cortinarius mushroom intoxication
The structures of orellanine and orelline
Photodeposition of orellanine and orelline, the fungal toxins of Cortinarius orellanus (Fries) and Cortinarius speciosissimus
A revised checklist of poisonous mushrooms in China
Ectomycorrhizal Cortinarius species participate in enzymatic oxidation of humus in northern forest ecosystems
Acute renal failure following collective intoxication by Cortinarius orellanus
Acute renal failure due to Cortinarius poisoning
Orellanine specifically targets renal clear cell carcinoma
Voluntary ingestion of Cortinarius mushrooms leading to chronic interstitial nephritis
New advances in researches on poisonous mushrooms since 2000
Investigation and analysis of 102 mushroom poisoning cases in southern China from 1994 to 2012
Structures of an orellanine-trifluoroacetic acid comples: evidence of a very short O-H···O hydrogen bond
Acute renal insufficiency and pancreatitis in a child with atypical Henoch-Schönlein purpura: efficacy of a single dose of cyclophosphamide
Main features of Cortinarius spp. poisoning: a literature review
Shifts in ectomycorrhizal fungal communities and exploration types relate to the environment and fine-root traits across interior Douglas-fir forests of western Canada
DOI:10.3389/fpls.2019.00643
URL
PMID:31191571
[本文引用: 1]

Large-scale studies that examine the responses of ectomycorrhizal fungi across biogeographic gradients are necessary to assess their role in mediating current and predicted future alterations in forest ecosystem processes. We assessed the extent of environmental filtering on interior Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii var. glauca (Beissn.) Franco) ectomycorrhizal fungal communities across regional gradients in precipitation, temperature, and soil fertility in interior Douglas-fir dominated forests of western Canada. We also examined relationships between fine-root traits and mycorrhizal fungal exploration types by combining root and fungal trait measurements with next-generation sequencing. Temperature, precipitation, and soil C:N ratio affected fungal community dissimilarity and exploration type abundance but had no effect on alpha-diversity. Fungi with rhizomorphs (e.g., Piloderma sp.) or proteolytic abilities (e.g., Cortinarius sp.) dominated communities in warmer and less fertile environments. Ascomycetes (e.g., Cenococcum geophilum) or shorter distance explorers, which potentially cost the plant less C, were favored in colder/drier climates where soils were richer in total nitrogen. Environmental filtering of ectomycorrhizal fungal communities is potentially related to co-evolutionary history between Douglas-fir populations and fungal symbionts, suggesting success of interior Douglas-fir as climate changes may be dependent on maintaining strong associations with local communities of mycorrhizal fungi. No evidence for a link between root and fungal resource foraging strategies was found at the regional scale. This lack of evidence further supports the need for a mycorrhizal symbiosis framework that is independent of root trait frameworks, to aid in understanding belowground plant uptake strategies across environments.
Synthesis of orellanine, the lethal poison of a toadstool
Human and experimental toxicology of orellanine
Acute renal failure following ingestion of Cortinarius orellanus in 12 patients. Initial presentation and progress over a period of 13 years
Renal involvement in mushroom poisoning: the case of orellanus syndrome
BRAF inhibition sensitizes melanoma cells to α-amanitin via decreased RNA polymerase II assembly
DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-44112-7
URL
PMID:31123282
[本文引用: 1]

Despite the great success of small molecule inhibitors in the treatment of patients with BRAF(V600E) mutated melanoma, the response to these drugs remains transient and patients eventually relapse within a few months, highlighting the need to develop novel combination therapies based on the understanding of the molecular changes induced by BRAF(V600E) inhibitors. The acute inhibition of oncogenic signaling can rewire entire cellular signaling pathways and thereby create novel cancer cell vulnerabilities. Here, we demonstrate that inhibition of BRAF(V600E) oncogenic signaling in melanoma cell lines leads to destabilization of the large subunit of RNA polymerase II POLR2A (polymerase RNA II DNA-directed polypeptide A), thereby preventing its binding to the unconventional prefoldin RPB5 interactor (URI1) chaperone complex and the successful assembly of RNA polymerase II holoenzymes. Furthermore, in melanoma cell lines treated with mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitors, alpha-amanitin, a specific and irreversible inhibitor of RNA polymerase II, induced massive apoptosis. Pre-treatment of melanoma cell lines with MAPK inhibitors significantly reduced IC50 values to alpha-amanitin, creating a state of collateral vulnerability similar to POLR2A hemizygous deletions. Thus, the development of melanoma specific alpha-amanitin antibody-drug conjugates could represent an interesting therapeutic approach for combination therapies with BRAF(V600E) inhibitors.
Efficiency of haemoperfusion materials at removing the fungal toxin orellanine from human plasma
Intoxication collective de type orellanien provoquee par Cortinarius splendens R. Hy
Antioxidant treatment and outcome of Cortinarius orellanus poisoning: a case series
DOI:10.3109/0886022X.2013.826110
URL
PMID:23968303
[本文引用: 1]

OBJECTIVES: To study the frequency, severity, and long-term outcome of renal injury in Cortinarius orellanus poisoning, to evaluate the association between the ingested amount of C. orellanus and outcome, and to evaluate the effect of N-acetylcysteine and corticosteroid treatment on outcome. METHODS: Case series of eight patients. Diagnosis and severity of acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) were classified according to current AKI and CKD definitions. N-acetylcysteine and corticosteroids were administered to six patients, former according to the standard for paracetamol poisoning. MAIN FINDINGS: All patients developed AKI, six in the most severe stage and four required renal replacement therapy (RRT). After 12 months, seven patients presented with CKD, of whom three required chronic RRT and further two were in advanced CKD. AKI and CKD severity highly correlated with the consumed amounts of Cortinarius orellanus (r = 0.98, p < 0.001 and r = 0.78, p = 0.02, respectively) but not with N-acetylcysteine and corticosteroid treatment. CONCLUSIONS: AKI and CKD by current definitions and classifications are frequent and severe after Cortinarius orellanus poisoning. The ingested amount of Cortinarius orellanus correlates with the severity of both AKI and CKD. N-acetylcysteine and corticosteroid treatment do not seem to have a beneficial effect on either AKI or CKD.
Erfahrungen mit Derrnocybe orellana (Fr.) in Polen. B. Massenvergiftung durch den orangefuchsigen Hautkopf
L’isolement de l’orellanine poison du Cortinarius orellanus Fries et l’etude de ses effets anatomo - pathologiques
NC-001 induces apoptosis and necrosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma in vitro and in a xenograft model in vivo
Long-term clinical outcome for patients poisoned by the fungal nephrotoxin orellanine
Analysis of the mushroom nephrotoxin orellanine and its glucosides
DOI:10.1021/np300135k
URL
PMID:23046414
[本文引用: 3]

Orellanine is a nephrotoxin found in various Cortinaceae mushroom species. Unintentional consumption after these species were confused with edible mushrooms such as Cantharellus tubaeformis has caused several casualties. In this work, a quantitative HPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for total orellanine in Cortinarius rubellus, spiked blood plasma, and a mushroom stew prepared from C. tubaeformis with the addition of a single specimen of C. rubellus is presented. The existence of mono- and diglucosylated orellanine in C. rubellus was also proven, although quantitative analysis could not be obtained for the glucosides due to rapid hydrolyzation to orellanine in the extract. Extraction with 3 M HCl or water mainly yielded orellanine, while MeOH or acidified MeOH mainly extracted mono- and diglucosylated orellanine. The highest recovery of total orellanine was obtained with 3 M HCl, which was subsequently used for quantitative analysis. A C(1)(8) HPLC column and low pH in the eluents retained all these toxins. Orellanine could be detected at a 4.9 ng/mL level in all extracts, which is well below the threshold for acute toxic effects. Additionally, the fragmentation pattern of orellanine upon electrospray MS/MS was probed. The method described is useful for two important applications. First, it allows quantitative analysis of processed food products that may be contaminated by orellanine from Cortinaceae mushrooms. Second, orellanine is currently being evaluated as a potential cure of metastatic renal cancer, and this work provides a method for monitoring orellanine at low concentrations within the therapeutic interval in blood serum.
Isolation and nephrotoxic studies of orellanine from the mushroom Cortinarius speciossismus
DOI:10.1016/0041-0101(87)90241-8
URL
PMID:3576636
[本文引用: 3]

A nephrotoxic substance has been isolated from Cortinarius speciosissimus. The 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR mass spectra indicated the chemical structure to be 3,3',4,4'-tetrahydroxy-2,2'-bipyridine-N-N'-dioxide. The toxin was quantitated using reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. The detection limit of this method was 500 pg, corresponding to a signal-to-noise ratio of 2.5. The toxin had an LD50 in mice of approximately 20 mg/kg i.p. Light microscopic examination of the kidneys of mice surviving treatment with the toxin showed interstitial nephritis and tubular necrosis.
Renal transplantation after Cortinarius speciosissimus poisoning. Nephrology, Dialysis,
Ingestion of a newly described North American mushroom species from Michigan resulting in chronic renal failure: Cortinarius orellanosus
DOI:10.3109/15563650.2010.495346 URL [本文引用: 1]
Orellanine and other fluorescent compounds in the genus Cortinarius, section Orellani
DOI:10.1080/00275514.1985.12025156 URL [本文引用: 1]
High-dose antioxidant therapy and steroids might improve the outcome of acute renal failure from intoxication by Cortinarius rubellus: report of two cases
DOI:10.1093/ckj/sfs129
URL
PMID:26069805
[本文引用: 2]

Only a small number of cases with favourable outcome after acute renal failure due to intoxication by Cortinarius sp. have been reported in the literature, and approximately half of the patients develop chronic renal failure and dialysis-dependency. We report the case of a couple with acute renal failure after accidental intake of Cortinarius rubellus and a favourable outcome after treatment with high-dose antioxidant therapy with N-acetylcysteine and steroids. Dialysis was never necessary in both patients and renal function was almost normal at the end of follow-up. Underdiagnosis of this rare cause of acute renal failure is likely due to the fact that affected patients develop symptoms of intoxication after a delay of 2-30 days. In patients with unclear acute renal failure with or without gastrointestinal symptoms, intoxication from Cortinarius sp. should be considered as a differential diagnosis. Early treatment with high-dose antioxidant therapy and steroids might be effective in reducing the risk of chronic renal failure.
Acute renal failure from intoxication by Cortinarius orellanus: recovery using anti-oxidant therapy and steroids
DOI:10.1093/ndt/14.11.2779-a URL PMID:10534536 [本文引用: 2]
The presence of orellanine in spores and basidiocarp from Cortinarius orellanus and Cortinarius rubellus
α-amanitin restrains cancer relapse from drug-tolerant cell subpopulations via TAF15
DOI:10.1038/srep25895
URL
PMID:27181033
[本文引用: 1]

Cancer relapse occurs with substantial frequency even after treatment with curative intent. Here we studied drug-tolerant colonies (DTCs), which are subpopulations of cancer cells that survive in the presence of drugs. Proteomic characterization of DTCs identified stemness- and epithelial-dominant subpopulations, but functional screening suggested that DTC formation was regulated at the transcriptional level independent from protein expression patterns. We consistently found that alpha-amanitin, an RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) inhibitor, effectively inhibited DTCs by suppressing TAF15 expression, which binds to RNA to modulate transcription and RNA processing. Sequential administration of alpha-amanitin and cisplatin extended overall survival in a cancer-relapse mouse model, namely peritonitis carcinomatosa. Therefore, post-treatment cancer relapse may occur through non-distinct subpopulations and may be effectively prevented by alpha-amanitin to disrupt transcriptional machinery, including TAF15.
Cortinarius section Bicolores and section Saturnini (Basidiomycota, Agaricales), a morphogenetic overview of European and North American species
DOI:10.3767/persoonia.2017.39.08
URL
PMID:29503475
[本文引用: 1]

Cortinarius is the largest genus of ectomycorrhizal fungi worldwide. Recent molecular studies have shown high levels of morphological homoplasy within the genus. Importantly, DNA phylogenies can reveal characteristics that have been either over- or underemphasized in taxonomic studies. Here we sequenced and phylogenetically analysed a large set of pan-European and North American collections taxonomically studied and placed in Cortinarius sect. Bicolores and sect. Saturnini, according to traditional morpho-anatomical criteria. Our goal was to circumscribe the evolutionary boundaries of the two sections, to stabilize both the limits and nomenclature of relevant species, and to identify described taxa which, according to our current understanding, belong to other lineages. Our analysis resolves two clades: /Bicolores, including 12 species, one of which is new to science, and /Saturnini, including 6 species. Fifteen binomials, traditionally treated in these two sections based on morphology, do not belong to the above two phylogenetic clades. Instead, six of these latter are clearly placed in other clades that represent sect. Bovini, sect. Sciophylli, sect. Duracini and sect. Brunneotincti. The presence or absence of blue pigments and the detection of specific odours emerge as clearly misleading taxonomic features, but more surprisingly, spore size and ecology can be misleading as well. A total of 63 type specimens were sequenced, 4 neotypes and 2 epitypes are proposed here, and 1 new combination is made.
Cortinarius section Thaumasti in South American Nothofagaceae forests
DOI:10.1080/00275514.2019.1689748
URL
PMID:31900077
[本文引用: 1]

Medicinal Ganoderma mushrooms have long tradition in Asia, and recently they began to be consumed in Europe as well. Among hundreds of Ganoderma species, only a few of them are intensively investigated, i.e., G. lucidum and G. applanatum, whereas the chemistry and bioactivities of the other species, especially of European origin, still remain unknown. This study comprises detailed chemical analysis of two Ganoderma species growing wild in Turkey, G. pfeifferi and G. carnosum. Metal composition of both species shows high concentrations of biogenic metals. Phenolic composition of the isolated extracts of G. carnosum and G. pfeifferi shows that these species are rich in simple phenolic acids, such as 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid and vanillic acid, but also in flavonoids. These compounds are found to be carriers of the antioxidant activity but also enzyme inhibition activity of the analyzed extracts. Overall results indicate that these two Ganoderma species have strong potential to be used for medicinal purposes.
A new way to target p53-defective colorectal cancer
DOI:10.2217/fon.15.223 URL PMID:26549592 [本文引用: 1]
TP53 loss creates therapeutic vulnerability in colorectal cancer
DOI:10.1038/nature14418
URL
PMID:25901683
[本文引用: 1]

TP53, a well-known tumour suppressor gene that encodes p53, is frequently inactivated by mutation or deletion in most human tumours. A tremendous effort has been made to restore p53 activity in cancer therapies. However, no effective p53-based therapy has been successfully translated into clinical cancer treatment owing to the complexity of p53 signalling. Here we demonstrate that genomic deletion of TP53 frequently encompasses essential neighbouring genes, rendering cancer cells with hemizygous TP53 deletion vulnerable to further suppression of such genes. POLR2A is identified as such a gene that is almost always co-deleted with TP53 in human cancers. It encodes the largest and catalytic subunit of the RNA polymerase II complex, which is specifically inhibited by alpha-amanitin. Our analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) databases reveals that POLR2A expression levels are tightly correlated with its gene copy numbers in human colorectal cancer. Suppression of POLR2A with alpha-amanitin or small interfering RNAs selectively inhibits the proliferation, survival and tumorigenic potential of colorectal cancer cells with hemizygous TP53 loss in a p53-independent manner. Previous clinical applications of alpha-amanitin have been limited owing to its liver toxicity. However, we found that alpha-amanitin-based antibody-drug conjugates are highly effective therapeutic agents with reduced toxicity. Here we show that low doses of alpha-amanitin-conjugated anti-epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) antibody lead to complete tumour regression in mouse models of human colorectal cancer with hemizygous deletion of POLR2A. We anticipate that inhibiting POLR2A will be a new therapeutic approach for human cancers containing such common genomic alterations.
Poisonous mushrooms and their toxins in China
Lack of efficacy of early plasma exchange in renal toxicity from Cortinarius orellanus
DOI:10.1159/000045288 URL PMID:9933767 [本文引用: 1]
Neuere Erkennmisse fiber Pilzgifte und Giftpilze
Acute renal failure following ingestion of wild mushrooms
DOI:10.1046/j.1444-0903.2001.00199.x
URL
PMID:11951934
[本文引用: 1]

We describe three cases of acute renal failure in young men who ingested wild mushrooms with the intent of producing hallucinations. Two cases remained dialysis dependent and, in these cases, renal biopsy revealed tubulointerstitial nephritis and fibrosis. Similar cases have been reported in other countries, but not in Australia. The most recognized mushroom nephrotoxin is orellanine, however the causative mushroom species and the actual toxin involved in these cases are unknown.
Successful living related kidney transplantation for end-stage renal failure caused by orellanine syndrome
DOI:10.1093/qjmed/hcs201 URL PMID:23097388 [本文引用: 1]
Pharmacokinetic properties of the nephrotoxin orellanine in rats
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the experimental inflammation induced by the toxic mushroom Cortinarius speciosissimus in the rat kidney
DOI:10.1016/s0014-4908(76)80040-3
URL
PMID:991966
[本文引用: 1]

A single intraperitoneal dose of cyclophosphamide (150 mg/kg) given at the same time as an oral dose of Cortinarius speciosissimus prevented the renal inflammation induced by this toxic mushroom in the male rat. Furthermore, a scar formation around dilated collecting ducts was clearly reduced by cyclophosphamide treatment. In general the only lesions observed in the cyclophosphamide treated animals were dilated collecting ducts in the outer medullary zone, the epithelia of which were either in regenerative mitosis or were atrophic. Apparently the primary sites of action of Cortinarius toxins in male rats are the collecting ducts of the outer medullary zone. When inflammation and the subsequent scar formation is prevented by cyclophosphamide, the damaged tubules can regenerate by mitotic activity and perhaps restore normal function.
The fungal nephrotoxin orellanine simultaneously increases oxidative stress and down-regulates cellular defenses
DOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.01.017
URL
PMID:18279679
[本文引用: 2]

Confusion of various nephrotoxic Cortinarius species with edible mushrooms occurs every year throughout Europe and North America. The toxin, orellanine (OR), accumulates selectively in renal tubular epithelium with ensuing renal failure after several days as the only clinical manifestation. This study was performed to clarify the mechanisms behind the kidney damage. Sprague-Dawley rats, 100 g bw, received various doses of purified OR ip (0-5 mg/kg bw). One week later, renal function (GFR) was determined (51Cr-EDTA), ascorbyl radicals in venous blood were analyzed using electron spin resonance, and oxidative protein damage was evaluated immunohistochemically. One OR-treated group (3.5 mg/kg) simultaneously received superoxide dismutase (SOD) targeted to tubular epithelium (HC-SOD; 10 mg/kg ip daily for 5 days). RT-PCR was used for analysis of mRNA expression of genes related to oxidative stress. OR caused a dose-dependent decrease in GFR, paralleled by increased levels of ascorbyl radicals and oxidative protein damage. Antioxidant treatment with HC-SOD decreased renal function even more and also increased tissue damage and mortality. Renal mRNA levels for key components in the antioxidative defense were strongly decreased, whereas those for several cytokines were increased. The data strongly suggest that OR nephrotoxicity in vivo is mediated by oxidative stress, including a virtual shutdown of important antioxidative enzymes. We interpret the unexpected effect of HC-SOD in terms of unbalanced SOD and catalase levels in the presence of OR, leading to massive generation of *OH and cell death.
Cortinarius sect. Armillati in northern Europe
DOI:10.3852/10-350
URL
PMID:21498554
[本文引用: 1]

Cortinarius sect. Armillati (subgenus Telamonia) was studied extensively based on morphology and molecular data. A total of about 1000 specimens, mostly from Fennoscandia, were revised. The nomenclature of the species was confirmed by sequencing the type material. Phylogenetic relationships were inferred by analyses of ITS, and the results were compared with the morphological and ecological data. Based on macro- and micromorphological characters, as well as molecular data, section Armillati contains only the medium to large species with slightly hygrophanous pileus and +/- reddish or in some species yellowish brown to rose brown universal veils. The other red-brown-veiled species, previously included in Armillati, seem to belong to at least seven different sections or clades: sect. Anthracini, sect. Boulderenses, sect. Brunneotincti p.p., sect. Cinnabarini, sect. Fulvescentes, /Fuscoperonatus, and /Praestigiosus. Our study recognized six Armillati species from northern Europe: C. armillatus, C. luteo-ornatus, C. paragaudis, and three species described as new, C. pinigaudis, C. roseoarmillatus, and C. suboenochelis. The former three also occur in North America. Two additional species, C. subarmillatus (Japan) and C. quercoarmillatus (Costa Rica), are known outside the area. Based on the phylogenetic analysis, the species associated with deciduous trees, C. armillatus, C. quercoarmillatus, and C. roseoarmillatus, all with dextrinoid, thick-walled spores, formed a separate group from the mainly conifer-associated species, C. luteo-ornatus, C. paragaudis, C. pinigaudis and C. suboenochelis, all with fairly thin to moderately thick-walled, indextrinoid to moderately dextrinoid spores. Descriptions of the northern European species are provided, the distribution is mapped and their taxonomy, ecology, distribution, and relationships are discussed. A total of 64 new sequences of 12 species are reported including 17 sequences from type material. Our study also suggests that ITS sequences are not always sufficiently variable for species-rank recognition (barcoding) in Cortinarius.
Cortinarius subgenus Callistei in North America and Europe - type studies, diversity, and distribution of species
DOI:10.3852/16-033
URL
PMID:27549620
[本文引用: 1]

Five species of Cortinarius subgenus Callistei, are recognized in Europe and North America. Cortinarius callisteus, C. infucatus, and C. neocallisteus sp. nov. have a broad distribution, extending from western North America to Europe. Cortinarius tofaceus is known from eastern North America and Europe, while C. callistei sp. is known only from one locality in Sweden. All five species are primarily associated with coniferous trees. Previously the species were included either in subgenus Leprocybe or subgenus Cortinarius, but recently they have been separated into subgenus Callistei based on molecular data. Type specimens of the names associated with this subgenus were studied and a neotype proposed for C. tofaceus and an epitype for C. infucatus Barcodes for the species are deposited in RefSeq and UNITE.
Peroxidase-mediated oxidation, a possible pathway for activation of the fungal nephrotoxin orellanine and related compounds. ESR and spin-trapping studies
DOI:10.3109/10715769809066887
URL
PMID:9702530
[本文引用: 2]

Orellanine is the tetrahydroxylated and di-N-oxidized bipyridine toxin extracted from several Cortinarius mushrooms among them C. orellanus. The pathogenic mechanism involved in the C. orellanus-poisoning by orellanine leading to kidney impairment is not yet fully understood until now. Electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy has been used to study the activation of orellanine by horseradish peroxidase/H2O2 system at physiological pH. Evidence for a one-electron oxidation of the toxin by this enzymatic system to an ortho-semiquinone radical intermediate is presented. The orellanine ortho-semiquinone generated by the peroxidase/H2O2 system abstracts hydrogen from glutathione, generating the glutathionyl radical which is spin-trapped by 5,5'-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO) and subsequently detected by ESR spectroscopy. Similarly, the ortho-semiquinone abstracts hydrogen from ascorbic acid to generate the ascorbyl radical which is detected by direct ESR. The peroxidatic oxidation of orellanine to semiquinone followed by its reduction by glutathione or ascorbic acid does not induce dioxygen uptake. The relationship between chemical structure and HRP oxidation of orellanine-related molecules, namely orelline and DHBPO2 (the parent molecule lacking of hydroxyl groups in 3 and 3' position) has been investigated in absence or in presence of reducing agents. None of the orellanine-related compounds can be oxidized by the HRP/H2O2 system, showing that both catecholic moieties and aminoxide groups are necessary for observing the formation of the ortho-semiquinone form of orellanine. As shown for the (photo)chemical oxidation of orellanine, the mechanism of toxicity could be correlated with a depletion of glutathione and ascorbate levels which are implicated in the defence against oxidative damage.
Novel methods for identification and quantification of the mushroom nephrotoxin orellanine. Thin-layer chromatography and electrophoresis screening of mushrooms with electron spin resonance determination of the toxin
DOI:10.1016/S0021-9673(96)00695-4 URL [本文引用: 2]
Unveiling new sequestrate Cortinarius species from northern Patagonian Nothofagaceae forests based on molecular and morphological data
DOI:10.1080/00275514.2018.1537350
URL
PMID:30676893

Because of systematic sampling campaigns in the northern Patagonian Nothofagaceae forests of Argentina, several specimens of sequestrate fungi were collected. Some of those collections showed phylogenetic affinities and morphological similarities to members of the formerly recognized sequestrate genus Thaxterogaster, currently a synonym of Cortinarius on the basis of molecular data. Comparisons of macro- and micromorphological features and sequences of nuc rDNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions have revealed that these collections belong to formerly undescribed species. The sequences of the four new taxa presented here, Cortinarius flavopurpureus, C. translucidus, C. nahuelhuapensis, and C. infrequens, were combined into a data set including additional sequences generated from herbarium collections and retrieved from public gene databases and analyzed by maximum likelihood and Bayesian inference methods. The four new species were resolved as distinct clades with strong support; at the same time, they showed unique morphological characteristics (hypogeous to subhypogeous habit, complete gasteromycetation, and spore shape and ornamentation) that separate them from previously described Cortinarius species. In addition, several undescribed and/or not previously sequenced species from these forests were detected through phylogenetic analysis of ectomycorrhizal root tip sequences. A key of characters to identify the sequestrate Cortinarius from Patagonia is provided.
Renal failure after eating “magic” mushrooms
Chemotaxonomic study of orellanine in species of Cortinarius and Dermocybe
DOI:10.1080/00275514.1988.12025612 URL [本文引用: 1]
Orellanine inhibits protein synthesis in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells, in rat liver mitochondria, and in vitro: indication for its activation prior to in vitro inhibition
DOI:10.1016/0300-483x(91)90163-u
URL
PMID:1708173
[本文引用: 1]

Pure orellanine, a nephrotoxic compound extracted from the mushroom Cortinarius orellanus, which is known to induce severe kidney damage several days or weeks after ingestion, is found to inhibit strongly the synthesis of macromolecules (proteins, RNA and DNA) in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells and in rat liver mitochondria, although the uptake of labelled precursors of the above macromolecules is not significantly altered. Direct addition of orellanine to a cell-free system of rabbit reticulocyte lysate does not produce any inhibition of protein synthesis. However, when orellanine is pre-incubated with activating rat liver microsomal systems, this inhibition occurs. Thus, the in vivo inhibition of protein synthesis is most likely due to a metabolite of orellanine.
Differential inhibitory action of the fungal toxin orellanine on alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes
DOI:10.1016/0304-4165(89)90117-7
URL
PMID:2566329
[本文引用: 1]

The inhibitory action of orellanine (3,3',4,4'-tetrahydroxy-2,2'-dipyridyl-1,1'-dioxide), a fungal toxin of Cortinarius orellanus Fr. and C. orellanoides R. Hry., on alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes was studied. Orellanine specifically inhibited alkaline phosphatase activity in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cell cultures and in the colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 without affecting gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity. Kinetic studies revealed that orellanine acts on renal alkaline phosphatase as a noncompetitive inhibitor, whereas the intestinal and placental isoforms are inhibited competitively.
New species of Cortinarius sect. Austroamericani, sect. nov., from South American Nothofagaceae forests
DOI:10.1080/00275514.2018.1515449
URL
PMID:30489223
[本文引用: 3]

In this study, we document and describe the new Cortinarius section Austroamericani. Our results reveal high species diversity within this clade, with a total of 12 recognized species. Of these, only C. rufus was previously documented. Seven species are described as new based on basidiomata collections. The four remaining species are only known from environmental sequences. All examined species form ectomycorrhizal associations with species of Nothofagaceae and are currently only known from Argentinean and Chilean Patagonia. The phylogenetic analysis based on the nuc rDNA internal transcriber spacer (ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 = ITS) and partial 28S gene (28S) sequences shows that this section is related to other taxa from the Southern Hemisphere. Species in this group do not belong to subg. Telamonia, where C. rufus was initially placed. Cortinarius rufus and the newly described C. subrufus form a basal clade within sect. Austroamericani that has a weakly supported relationship with the core clade. Because the two species are morphologically similar to species from the core clade and share their distribution and Nothofagaceae associations, we include them here as part of sect. Austroamericani sensu lato (s.l.) until more material is available to refine the delimitation.
Mushroom poisoning caused by species of the genus Cortinarius (Fries)
DOI:10.1007/BF00302720
URL
PMID:6349583

Symptomatology, clinical characteristics and pathogenesis of mushroom poisoning caused by Cortinarius species are surveyed. The isolation of a bipyridine--orellanine--from Cortinarius orellanus is held to be responsible for the nephrotoxicity of this species as well as the closely related C. speciosissimus. The present knowledge on the toxicity of structurally related and well-known bipyridines such as paraquat and diquat is brought up and found comparable to orellanine toxicity. Pharmacokinetic experiments on the nephrotoxic bipyridines suggest that haemoperfusion is a rational therapy of intoxicated persons, even several days after mushroom ingestion.
Rituximab versus steroids and cyclophosphamide for the treatment of primary membranous nephropathy: protocol of a pilot randomised controlled trial
DOI:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-029232
URL
PMID:31806605
[本文引用: 1]

INTRODUCTION: Primary membranous nephropathy (MN) is a common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults. The disease may have different long-term outcomes. After 10 years of follow-up, 35%-50% of the untreated patients with persistent nephrotic syndrome may die or progress to end stage renal disease. The 2012 KDIGO (Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes) guidelines recommend that initial therapy should consist of alternating steroids and an alkylating agent for 6 months. Recent observational studies showed that the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab may be effective in inducing remission. We designed a pilot multicentre randomised trial to inform the design of a larger trial testing the efficacy and safety of treatment with steroids and cyclophosphamide versus rituximab in patients with primary MN and heavy proteinuria (>3.5 g/24 hours). METHODS AND ANALYSIS: This pilot, open-label, two-parallel-arm, randomised clinical trial will enrol 70 patients with primary MN and heavy proteinuria. Patients will be randomised in a 1:1 ratio to either the intervention arm (rituximab) or the active comparator arm (corticosteroid/alkylating-agent therapy). The study will provide estimates of the probability of complete remission of proteinuria and risk of serious side effects at 12 months to inform the design of a larger trial. We will also assess the recruitment potential of each participating centre to address study feasibility. ETHICS AND DISSEMINATION: The trial received ethics approval from the local ethics boards. We will publish pilot data to inform the design of a larger clinical trial. TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBERS: NCT03018535; 2011-006115-59.
A novel orellanine containing mushroom Cortinarius armillatus
DOI:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.02.010
URL
PMID:26915341
[本文引用: 4]

Orellanine (3,3',4,4'-tetrahydroxy-2,2'-bipyridine-1,1'-dioxide) is a tetrahydroxylated di-N-oxidized bipyridine compound. The toxin, present in certain species of Cortinarius mushrooms, is structurally similar to herbicides Paraquat and Diquat. Cortinarius orellanus and Cortinarius rubellus are the major orellanine-containing mushrooms. Cortinarius mushrooms are widely reported in Europe where they have caused human poisoning and deaths through accidental ingestion of the poisonous species mistaken for the edible ones. In North America, Cortinarius orellanosus mushroom poisoning was recently reported to cause renal failure in a Michigan patient. Cortinarius mushroom poisoning is characterized by delayed acute renal failure, with some cases progressing to end-stage kidney disease. There is debate whether other Cortinarius mushroom contain orellanine or not, especially in North America. Currently, there are no veterinary diagnostic laboratories in North America with established test methods for detection and quantitation of orellanine. We have developed two diagnostic test methods based on HPLC and LC-MSMS for identification and quantitation of orellanine in mushrooms. Using these methods, we have identified Cortinarius armillatus as a novel orellanine-containing mushroom in North America. The mean toxin concentration of 145 ug/g was <1% of that of the more toxic C. rubellus. The HPLC method can detect orellanine at 17 mug g(-1) while the LC-MSMS method is almost 2000 times more sensitive and can detect orellanine at 30 ng g(-1). Both tests are quantitative, selective and are now available for veterinary diagnostic applications.
Poisoning by Cortinarius speciosissimus
DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90653-6 URL PMID:14054451 [本文引用: 1]
Erfahrungen mit Dermocybe orellana (Fr.) in Polen. A. Cortinarius (Dermocybe) orellanus Fr. non Quel. - caused intoxications fongiques en Pologne en 1952-55
A phylogenetic approach to a global supraspecific taxonomy of Cortinarius (Agaricales) with an emphasis on the southern mycota
DOI:10.3767/persoonia.2019.42.10
URL
PMID:31551621
[本文引用: 1]

A section-based taxonomy of Cortinarius, covering large parts of the temperate North and South Hemispheres, is presented. Thirty-seven previously described sections are reviewed, while another forty-two sections are proposed as new or as new combinations. Twenty additional clades are recovered but not formally described. Furthermore, six new or combined species names are introduced, and one species is neotypified. The structure is supported by morphological characters and molecular evidence, based on two (nrITS and nrLSU) and four (nrITS, nrLSU, rpb1 and rpb2) loci datasets and analysed by Maximum Likelihood methods (PhyML, RAxML). Altogether 789 Cortinarius samples were included in the study.
Treatment of intoxication with Cortinarius speciosissimus using antioxidant therapy
DOI:10.1053/j.ajkd.2003.12.037
URL
PMID:15042564
[本文引用: 2]

The authors present the case reports of a 30-year-old man and his 29-year-old wife who ingested a mushroom meal containing Cortinarius speciosissimus. Features of this intoxication include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea as well as back pain. The toxin orellanine is nephrotoxic and can lead to acute renal failure. A long symptom-free interval of 2 to 21 days is characteristic of this poisoning. The diagnosis can be made by mycologic testing or by toxicologic analysis of a renal biopsy specimen. Reported therapeutic options include hemodialysis, plasmapheresis, or drug therapy with corticosteroids, all of which have yielded variable results. Here the authors report the use of antioxidant therapy in 2 patients with acute renal failure caused by Cortinarius speciosissimus intoxication.
Resource diversity of Chinese macrofungi: edible, medicinal and poisonous species
DOI:10.1007/s13225-019-00432-7 URL [本文引用: 2]
Peptides of pHLIP family for targeted intracellular and extracellular delivery of cargo molecules to tumors
Analysis of hazard in mushroom poisoning incidents in China mainland
2000年以来有毒蘑菇研究新进展
DOI:10.13346/j.mycosystema.140041
URL
[本文引用: 1]

误食毒蘑菇而中毒一直被认为是一个对人类健康造成威胁的全球性问题,也是我国食物中毒事件中导致死亡的最主要因素。对2000年以来在有毒蘑菇新种类、新毒素与新症状、有毒蘑菇鉴定及毒素检测新方法、有毒蘑菇中毒机理、毒素基因克隆、中毒治疗以及鹅膏肽类毒素治疗肿瘤等领域取得的新进展进行了综述,并对一些热点研究领域做了展望。
中国毒蘑菇名录
DOI:10.13346/j.mycosystema.130256
URL
[本文引用: 1]

根据文献报道和实际考察收录了我国毒蘑菇435种,对拉丁学名和中文名称进行了订正,文献常用的名称作为异名保留,纠正了以往文献中出现的毒蘑菇的拉丁学名,包括拼写错误和鉴定错误,同时列举出毒素成分及中毒类型,并引证了相关参考文献。