| 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列 Oligonucleotide sequence (5′→3′) | 目的 Use |
|---|---|---|
| pyrG/F | GCCAGTACGAGTGTTGTGGAG | 扩增pyrG基因片段 Amplification of pyrG gene fragments |
| pyrG/R | GTCAGACACAGAATAACTCTC | |
| 054800 5F/F | GGTATGGACTGGCATGGATAC | 融合 PCR 正向引物 Fusion PCR forward primers |
| 054800 3F/R | GTAATATCAAGACTGCGACGCG | 融合 PCR 反向引物 Fusion PCR reverse primers |
| 054800 5F/EF | CATTGAGGAACGATGCCATTAC | 扩增AflAZF1上游同源臂片段 Amplification of AflAZF1 upstream homology arm fragment |
| 054800 5F/R | GGGTGAAGAGCATTGTTTGAGGCGTCTTTGCTATCTACTCGTCTC | |
| 054800 3F/ER | CTTCAATTGATCGTGTTGACAC | 扩增AflAZF1下游同源臂片段 Amplification of AflAZF1 downstream homology arm fragments |
| 054800 3F/F | GCATCAGTGCCTCCTCTCAGACGCCGTACTGGTCTTCTGTTCG | |
| pyrG/TR | GTCTGAGAGGAGGCACTGATGC | ΔAflAZF1验证引物 ΔAflAZF1 validation primers |
| pyrG/TF | GCCTCAAACAATGCTCTTCACCC | |
| 054800 RT/F | GCCATTCACCTGTCTGTTGGAC | AflAZF1-ORF验证引物 AflAZF1-ORF validation primers |
| 054800 RT/R | CCTACGATCCTTTCCACGAC |
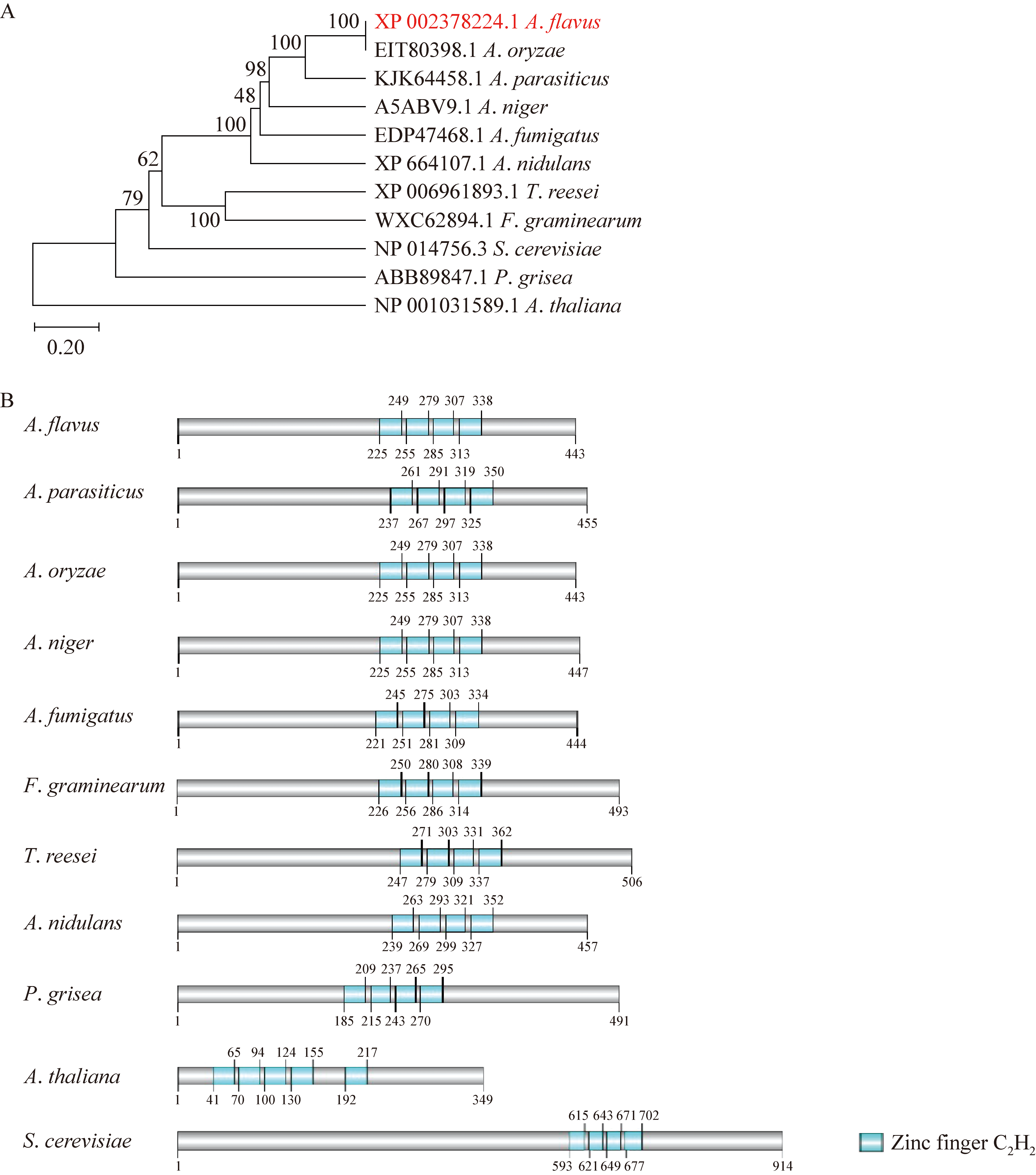 Fig. 1 The phylogenetic tree and domain analysis of the AZF1 proteins in Aspergillus flavus and other fungi. A: The phylogenetic tree of AZF1 proteins. The phylogenetic tree were constructed using MEGA7.0 software. The protein information is as follow: AflAZF1 (XP_002378224.1, A. flavus NRRL3357); AnAZF1 (A5ABV9.1, A. niger CBS 513.88); AfAZF1 (EDP47468.1, A. fumigatus A1163); TrAZF1 (XP_006961893.1, Trichoderma reesei QM6a); Azf1p (NP_014756.3, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C); CON1 (ABB89847.1, Pyricularia grisea); ApAZF1 (KJK64458.1, A. parasiticus); AoAZF1 (EIT80398.1, A. oryzae); AnAZF1 (XP_664107.1, A. nidulans); FgAZF1 (WXC62894.1, Fusarium graminearum); AtAZF1(GHJ86605.1, Arabidopsis thaliana). B: The domain of AZF1 proteins.
Fig. 1 The phylogenetic tree and domain analysis of the AZF1 proteins in Aspergillus flavus and other fungi. A: The phylogenetic tree of AZF1 proteins. The phylogenetic tree were constructed using MEGA7.0 software. The protein information is as follow: AflAZF1 (XP_002378224.1, A. flavus NRRL3357); AnAZF1 (A5ABV9.1, A. niger CBS 513.88); AfAZF1 (EDP47468.1, A. fumigatus A1163); TrAZF1 (XP_006961893.1, Trichoderma reesei QM6a); Azf1p (NP_014756.3, Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C); CON1 (ABB89847.1, Pyricularia grisea); ApAZF1 (KJK64458.1, A. parasiticus); AoAZF1 (EIT80398.1, A. oryzae); AnAZF1 (XP_664107.1, A. nidulans); FgAZF1 (WXC62894.1, Fusarium graminearum); AtAZF1(GHJ86605.1, Arabidopsis thaliana). B: The domain of AZF1 proteins.
 Fig. 2 Construction of AflAZF1 deletion mutant strain of Aspergillus flavus. A: Strategy of the construction of the AflAZF1 knockout mutant. B: PCR verification of WT (wild type) and ΔAflAZF1 strains. Knockout transformants are represented by T1, T2, T3, and T4; WT strain is the positive control; CK uses ddH2O as a template, serving as the negative control; Gel wells numbered P1, P2, and P3 represent the amplification results using primers P1, P2, and P3, respectively. Marker: DL2000.
Fig. 2 Construction of AflAZF1 deletion mutant strain of Aspergillus flavus. A: Strategy of the construction of the AflAZF1 knockout mutant. B: PCR verification of WT (wild type) and ΔAflAZF1 strains. Knockout transformants are represented by T1, T2, T3, and T4; WT strain is the positive control; CK uses ddH2O as a template, serving as the negative control; Gel wells numbered P1, P2, and P3 represent the amplification results using primers P1, P2, and P3, respectively. Marker: DL2000.
 Fig. 3 Effects of AflAZF1 in Aspergillus flavus on growth and conidial formation. A: Growth and conidial formation of the WT and ΔAflAZF1 strains. B: Statistical analysis of the colony diameter of WT and ΔAflAZF1 strains. Relative growth=colony diameter/wild-type colony diameter. C: Statistical analysis of the conidia produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1. Error bars represent the standard deviation of five replicates. * Indicates a significant difference between the WT and ΔAflAZF1 at 0.05 level; ** Indicate an extremely significant difference between the two strains at 0.01 level. The same below.
Fig. 3 Effects of AflAZF1 in Aspergillus flavus on growth and conidial formation. A: Growth and conidial formation of the WT and ΔAflAZF1 strains. B: Statistical analysis of the colony diameter of WT and ΔAflAZF1 strains. Relative growth=colony diameter/wild-type colony diameter. C: Statistical analysis of the conidia produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1. Error bars represent the standard deviation of five replicates. * Indicates a significant difference between the WT and ΔAflAZF1 at 0.05 level; ** Indicate an extremely significant difference between the two strains at 0.01 level. The same below.
 Fig. 5 AflAZF1 regulates the carbon source utilisation process in Aspergillus flavus. A: Growth of WT and ΔAflAZF1 on different carbon source media. B: Statistics analysis of colony diameters of WT and ΔAflAZF1 on eight types of carbon source media on day 5. C: Statistical analysis of conidia produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1.
Fig. 5 AflAZF1 regulates the carbon source utilisation process in Aspergillus flavus. A: Growth of WT and ΔAflAZF1 on different carbon source media. B: Statistics analysis of colony diameters of WT and ΔAflAZF1 on eight types of carbon source media on day 5. C: Statistical analysis of conidia produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1.
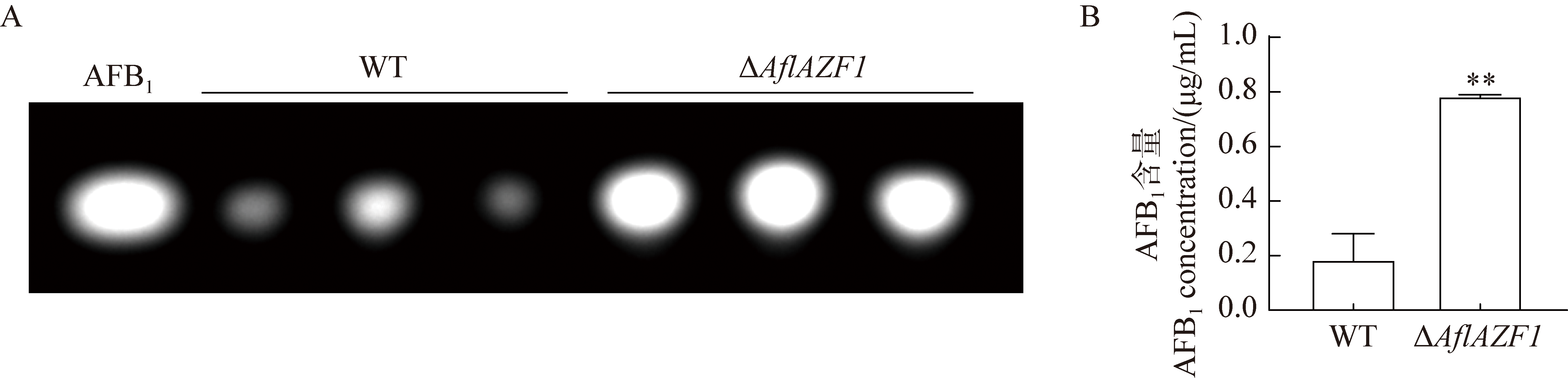 Fig. 7 AflAZF1 negatively regulates the AFB1 biosynthesis. A: TLC analysis of the production of AFB1 by WT and ΔAflAFZ1 on a YES medium. AFB1 is the standard aflatoxin. B: Quantitative analysis of the yield of AFB1 produced by WT and ΔAflAFZ1 on YES medium. Concentration of standard AFB1 is adjusted to 1 μg/mL, then the relative quantification of AFB1 was analyzed using GeneTools software. The same below.
Fig. 7 AflAZF1 negatively regulates the AFB1 biosynthesis. A: TLC analysis of the production of AFB1 by WT and ΔAflAFZ1 on a YES medium. AFB1 is the standard aflatoxin. B: Quantitative analysis of the yield of AFB1 produced by WT and ΔAflAFZ1 on YES medium. Concentration of standard AFB1 is adjusted to 1 μg/mL, then the relative quantification of AFB1 was analyzed using GeneTools software. The same below.
 Fig. 8 Effects of AflAZF1 on the pathogenicity of Aspergillus flavus. A: Growth of WT and ΔAflAZF1 strains on peanut. B: Quantitative analysis of the conidia produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1 on peanuts. C: TLC analysis of AFB1 from WT and ΔAflAZF1. D: Quantitative analysis of AFB1 produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1.
Fig. 8 Effects of AflAZF1 on the pathogenicity of Aspergillus flavus. A: Growth of WT and ΔAflAZF1 strains on peanut. B: Quantitative analysis of the conidia produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1 on peanuts. C: TLC analysis of AFB1 from WT and ΔAflAZF1. D: Quantitative analysis of AFB1 produced by WT and ΔAflAZF1.