冬虫夏草Ophiocordyceps sinensis (Berk.) G.H. Sung et al.是我国著名的药用真菌,主产于我国西藏、青海、四川、云南和甘肃等地,尼泊尔、不丹和印度也有分布(张永杰等 2010;张姝等 2013)。在我国有一千多年的药用历史,最早收载藏医经典著作《月王药诊》,其载曰:治肺部疾病;清本草《本草备要》:“保肺益肾,止血化痰,止劳咳”。冬虫夏草常被古代医家用于治疗肺和肾的疾病,如蛤蚧固金汤用于治疗肺肾并亏、喘咳痰血、将成劳损等,清金养血丹用于治疗男妇虚劳、夜热咳嗽、痰喘胸闷,咯血肠红等症(邱健健等 2020)。化学研究显示冬虫夏草含有核苷、氨基酸、甾醇、多糖和脂肪酸等化学成分(艾中等 2016;钱正明等 2016;李皓翔等 2020)。药理研究显示冬虫夏草在保护肾脏、肝脏,呼吸系统、生殖系统和心血管系统具有较好作用(Ji et al. 2009;Li et al. 2020;赵鹏等 2020)。
冬虫夏草补肾作用作为其主要功效被广泛应用于实际临床,如补肾培元胶囊、温肾全鹿丸和固本强身胶囊等均为冬虫夏草的复方中成药制剂具有能改善肾功能的作用。冬虫夏草在改善lgA肾病和糖尿病肾病的方面具有较好的作用(Wang et al. 2018;Xiao et al. 2018)。糖尿病肾病这类慢性肾脏疾病最终的共同特征是肾纤维化(Webster et al. 2017),肾纤维化是一种病理生理学改变,是肾功能从健康到损伤,到再损伤,最后丧失功能的一个渐进过程,前期药理结果表明冬虫夏草(发酵冬虫夏草菌Hirsutella sinensis)治疗肾纤维化是有效的(Pan et al. 2013;Du et al. 2015;潘秋霞等 2015)。但对冬虫夏草在肾纤维化治疗中的活性成分、靶点和作用机制尚未见报道。
网络药理学是基于现有的化学成分、药理信息和计算机信息来研究药物成分与复杂疾病的系统药理学(范卫锋等 2020;梁玉华等 2020)。网络药理学揭示了药物、靶点、疾病之间的关系,应用于系统阐明中医药的作用机制,并通过网络药理学研究进一步诠释药物治疗更多疾病的药理关系。庞欣欣等(2021)通过网络药理学分析出冬虫夏草通过抗炎、抗细胞凋亡等机制治疗膜性肾病。本研究旨在利用网络药理学的方法,获得冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化的有效成分,筛选出冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化的核心靶点和主要生物学途径,并进行分子对接,为探索冬虫夏草的作用机制提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 冬虫夏草主要活性化合物的筛选
在TCMSP、PubMed、CNKI等数据库中以Ophiocordyceps sinensis、Cordyceps sinensis、Chinese cordyceps和冬虫夏草为关键词检索冬虫夏草的化合物,以口服吸收利用度(OB)≥30%,药物类药性(DL)≥0.18为指标筛选,筛选后得到冬虫夏草的有效化合物。
1.2 冬虫夏草防治肾纤维化疾病靶点的收集和预测
在PubChem数据库查找筛选出的有效化合物的CAS号并下载3D分子结构的SDF格式文件,在TCMSP和STITCH数据库中筛选出的有效化合物的CAS号查找相应成分的靶点信息;将冬虫夏草有效化合物的SDF格式文件导入Swiss Target Prediction数据库预测冬虫夏草潜在作用靶点,合并以上3个数据库数据并删除重复项即可得到冬虫夏草潜在作用靶点。以renal fibrosis为关键词在GeneCard、OMIM和DisGeNET数据库检索与肾纤维化相关的靶点,合并以上3个数据库数据并删除重复靶点即可得到肾纤维化靶点;通过韦恩图R软件对冬虫夏草活性成分作用的靶点和肾纤维化靶点取交集并绘制韦恩图,获得冬虫夏草化合物作用于肾纤维化的靶点。
1.3 冬虫夏草活性成分-靶点网络的建立
用Cytoscape 3.7.2软件构建冬虫夏草有效化合物-靶点网络图。其中节点分别代表冬虫夏草活性成分、靶点;边代表活性成分与肾纤维化靶点相互作用关系。
1.4 冬虫夏草PPI网络图和频次分布图的构建
将1.2项筛选出的冬虫夏草肾纤维化靶点导入STRING网络平台,将蛋白种类定义为Homo sapiens进行筛选,获得蛋白互作网络图(PPI),使用R软件包统计冬虫夏草肾纤维化靶点在网络中的相互作用的频次,并绘制条形图展示关键靶点。
1.5 GO基因和KEGG通路富集分析
采用Bioconductor生物信息软件包,P<0.05,使用R语言软件包进行可视化处理,对冬虫夏草PPI靶点进行GO功能和KEGG通路富集分析,得到冬虫夏草成分作用主要靶点和潜在作用肾纤维化通路信号,对前20条目进行绘制气泡图。最后通过Cytoscape 3.7.2软件建立与肾纤维化密切相关的前20个信号通路-靶点-成分之间的相互作用网络。
1.6 分子对接
采用薛定谔分子对接软件Maestro 11.8对1.5项中预测靶点最多的成分与前6位的靶点进行分子对接验证,通过PubMed数据库获取活性成分的三维结构,在RCSB PDB网站下载受体蛋白,通过薛定谔分子对接软件Maestro 11.8对蛋白受体和小分子受体进行预处理后进行分子对接,获取对接结合能和对接图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 冬虫夏草活性成分的筛选
通过分析检索TCMSP数据库与相关文献(Yang et al. 2011;钱正明等 2016,2019;梅全喜和李文佳 2020)中的冬虫夏草化合物,共收集347个化合物,根据筛选条件OB≥30%和DL≥0.18进行筛选,得到可供进一步分析的有效化合物22个(表1)。
Table 1 The compounds of Chinese cordyceps
| 序号 No. | 名称 Name | CAS | MW | OB (%) | DL | 结构式 Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 醋酸豆甾醇 Stigmasterol 3-O-acetate | 4651-48-3 | 454.73 | 46.44 | 0.86 | |
| 2 | β-谷甾醇乙酸酯 β-Sitosteryl acetate | 915-05-9 | 456.74 | 40.39 | 0.85 | |
| 3 | 过氧化麦角甾醇 Peroxyergosterol | 2061-64-5 | 428.65 | 44.39 | 0.82 | |
| 4 | 啤酒甾醇 Cerevisterol | 516-37-0 | 430.66 | 39.52 | 0.77 | |
| 5 | 豆甾醇 Stigmasterol | 83-48-7 | 412.69 | 43.83 | 0.76 | |
| 6 | 麦角甾-4,6,8(14),22-四烯-3-酮 Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one | 19254-69-4 | 392.62 | 48.32 | 0.75 | |
| 7 | β-谷甾醇 β-Sitosterol | 201-480-6 | 414.71 | 36.91 | 0.75 | |
| 8 | 二氢菜籽甾醇 Dihydrobrassicasterol | 4651-51-8 | 400.68 | 37.58 | 0.71 | |
| 9 | 胆甾醇 Cholesterol | 57-88-5 | 386.65 | 37.87 | 0.68 | |
| 待续 | ||||||
| 10 | 金色酰胺醇酯 Aurantiamide acetate | 56121-42-7 | 444.52 | 58.02 | 0.52 | |
| 11 | 胆固醇棕榈酸酯 Cholesteryl hexadecanoate | 601-34-3 | 625.06 | 31.05 | 0.45 | |
| 12 | 1-Linoleoyl-3-palmitoyl-rac-glycerol | 99032-71-0 | 592.93 | 33.86 | 0.41 | |
| 13 | 酒渣碱 Flazin | 100041-05-2 | 308.29 | 94.28 | 0.39 | |
| 14 | 甘油单油酸酯 Glyceryl monooleate | 111-03-5 | 356.54 | 34.13 | 0.30 | |
| 15 | 川芎哚 Perlolyrine | 29700-20-7 | 264.28 | 65.95 | 0.27 | |
| 16 | 黄豆黄素 Glycitein | 40957-83-3 | 284.26 | 50.48 | 0.24 | |
| 17 | 单磷酸尿苷 Uridine monophosphate | 58-97-9 | 324.18 | 40.25 | 0.20 | |
| 18 | 11,14-二十碳二烯酸 11,14-Eicosadienoic acid | 2091-39-6 | 308.50 | 39.99 | 0.20 | |
| 19 | 亚油酸乙酯 Ethyl linoleate | 544-35-4 | 308.50 | 42.00 | 0.19 | |
| 20 | 维生素K1 Vitamin K1 | 84-80-0 | 450.70 | 47.60 | 0.66 | |
| 21 | 花生四烯酸 Arachidonic acid | 506-32-1 | 304.47 | 45.57 | 0.20 | |
| 22 | 乙酸亚油醇酯 Linoleyl acetate | 5999-95-1 | 308.50 | 42.10 | 0.20 |
2.2 冬虫夏草抗肾纤维化靶点
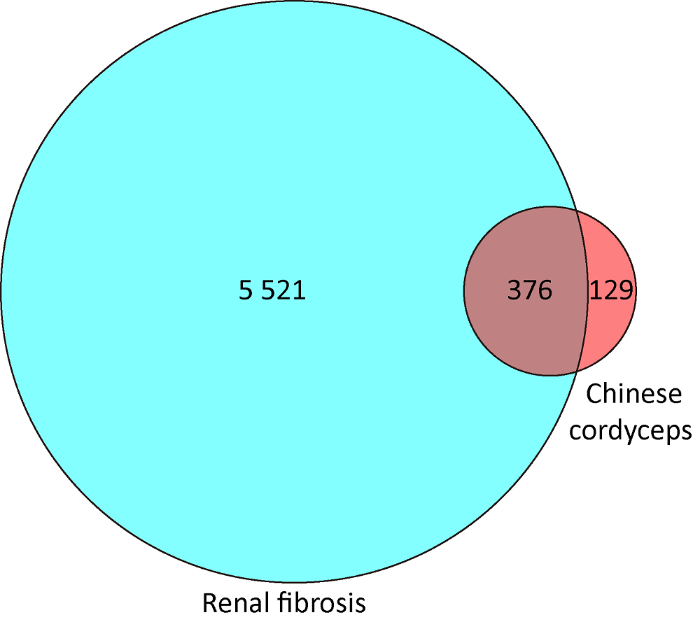
根据GeneCard、OMIM和DisGeNET数据库检索肾纤维化的相关基因,共有5 897个靶点。检索TCMSP、STITCH、Swiss target prediction等数据库得到冬虫夏草22个活性成分相关靶点505个,运用韦恩图R软件包得到冬虫夏草活性成分调控的靶点基因与肾纤维化的靶点基因交集,得到376个共同靶点(图1)。
图1
图1
冬虫夏草与肾纤维化靶点的韦恩图
Fig. 1
The Venn diagram of Chinese cordyceps and renal fibrosis targets.
2.3 冬虫夏草活性成分-靶点网络
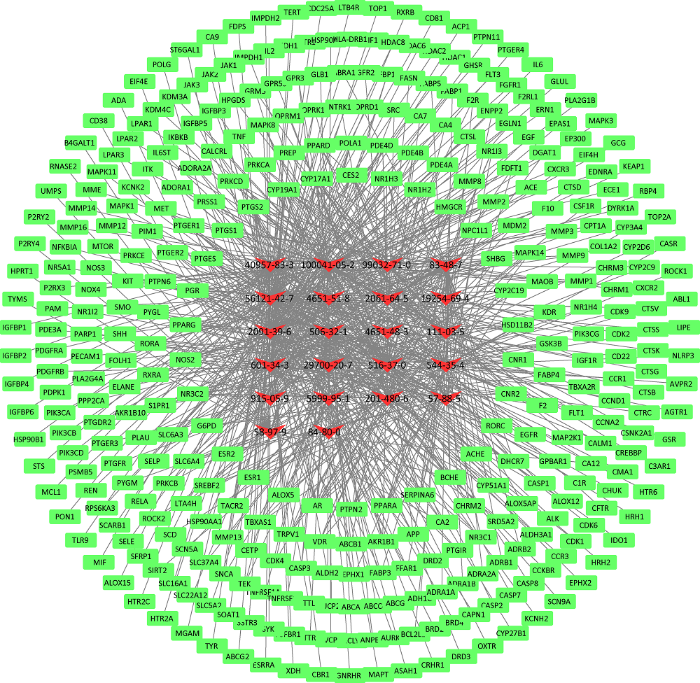
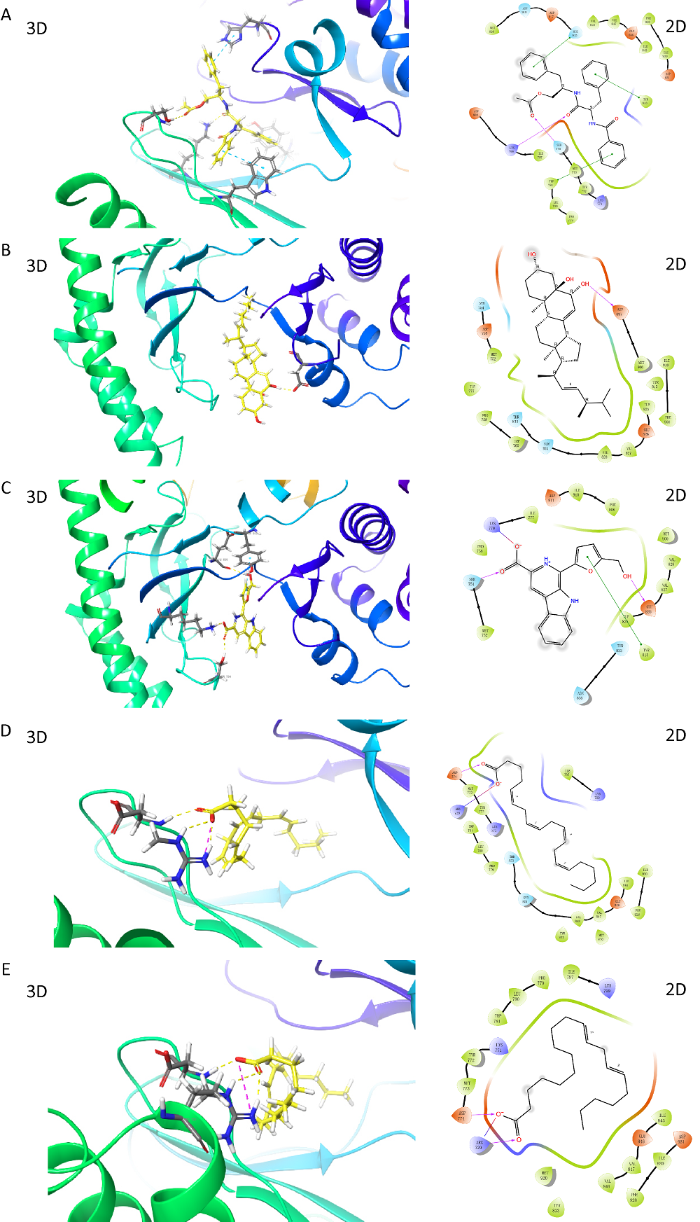
采用Cytoscape 3.7.2软件构建冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化症的化合物-靶点网络图(图2),红色“V”代表分子,绿色“四边形”代表靶蛋白,“边”代表冬虫夏草化合物与肾纤维化靶点相互作用关系。通过网络分析,金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、酒渣碱、11,14-二十碳二烯酸、花生四烯酸分别调控76、74、72、70和57个靶点,其可能为冬虫夏草抗肾纤维化的核心成分。
图2
2.4 冬虫夏草PPI网络和频次分布图
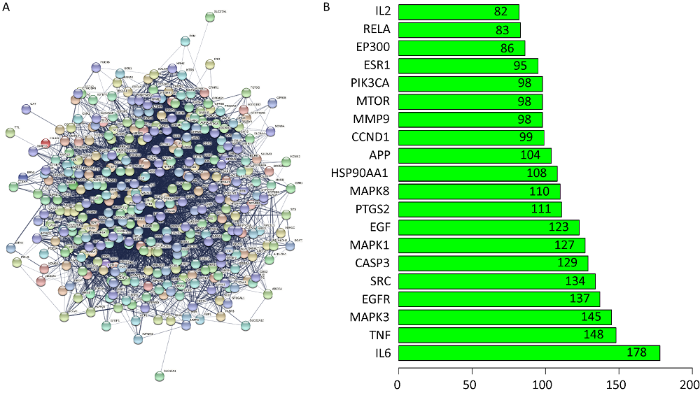
图3
图3
共同靶点PPI图和频次分布图
A:PPI网络图;B:前20个靶点的频次图
Fig. 3
Protein-protein interaction network.
A: PPI network of the common target genes; B: Frequency of the top 20 target genes.
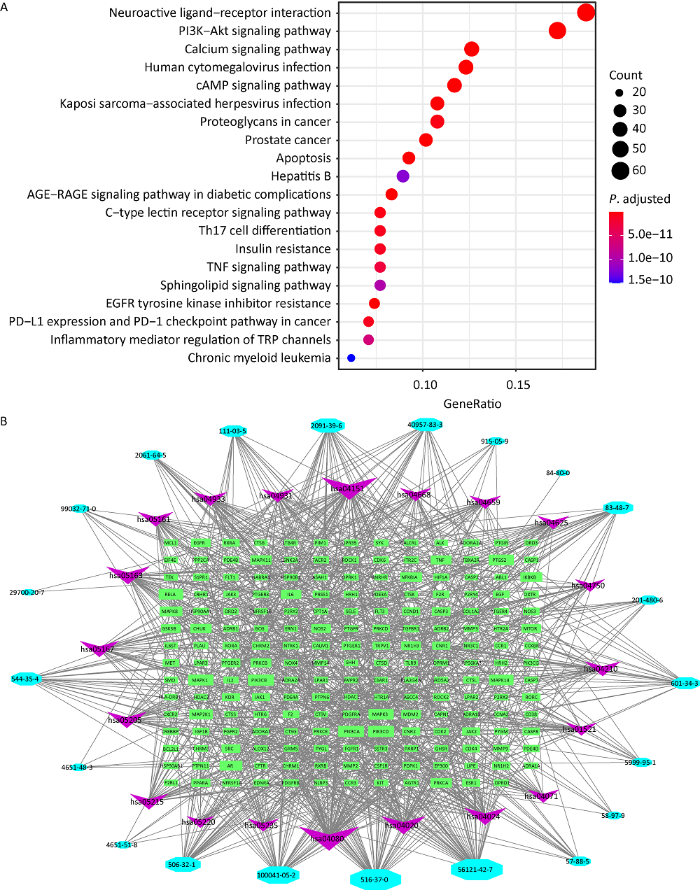
2.5 GO和KEGG通路富集分析
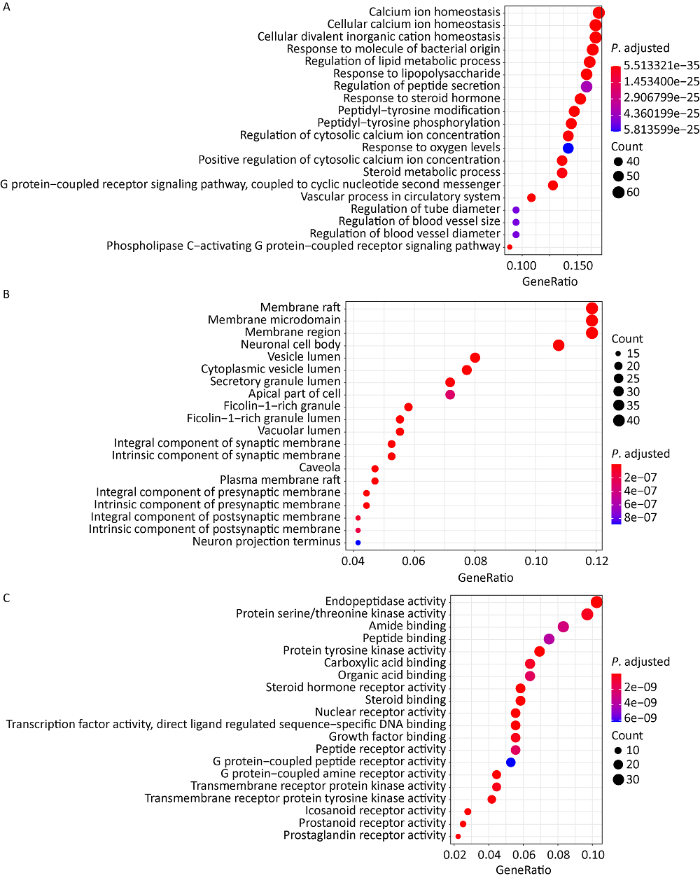
图4
图4
冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化靶点的GO富集图(前20个)
A:生物过程;B:细胞组分;C:分子功能
Fig. 4
GO enrichment analysis (top 20).
A: Biological processes; B: Cellular components; C: Molecular functions.
表2 冬虫夏草4个关键KEGG通路分析
Table 2
| ID | Pathway | Gene | Gene ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04080 | 神经活性配体- 受体相互作用 Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | ADRA1A, ADRA1B, ADRA2A, ADRB1, ADRB2, GABRA1, CHRM1, CHRM2, CHRM3, TRPV1, PRSS1, TACR2, CNR1, CNR2, S1PR1, PTGFR, PTGER3, PTGER1, ADORA1, ADORA2A, CALCRL, OPRM1, OPRK1, OPRD1, PTGER2, F2, CCKBR, GHSR, TBXA2R, SSTR3, F2RL1, CTSG, NR3C1, PTGIR, HTR1A, DRD2, P2RX3, GPR35, EDNRA, LPAR3, LPAR2, LPAR1, HTR2A, HTR2C, P2RY4, P2RY2, LTB4R, PTGER4, GCG, F2R, GRM5, AVPR2, AGTR1, C3AR1, HTR6, HRH1, HRH2, OXTR, DRD3, CRHR1, GNRHR | 61/327 |
| hsa04151 | PI3K-Akt 信号通路 PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | CDK2, CDK4, COL1A2, CCND1, GSK3B, HSP90AA1, MAPK1, CHRM1, CHRM2, NOS3, EGF, RXRA, RELA, PPP2CA, MDM2, EGFR, CSF1R, KIT, PRKCA, MTOR, MET, KDR, FGFR2, IKBKB, CHUK, NTRK1, PDGFRB, CDK6, SYK, JAK3, JAK1, JAK2, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CG, PIK3CA, IGF1R, FLT1, PDGFRA, PDPK1, FGFR1, MAP2K1, FLT3, TEK, HSP90AB1, LPAR3, LPAR2, LPAR1, BCL2L1, IL2, MCL1, HSP90B1, EIF4E, IL6, MAPK3, F2R | 56/327 |
| hsa04020 | 钙信号通路 Calcium signaling pathway | ADRA1A, ADRA1B, ADRB1, ADRB2, CALM1, CHRM1, CHRM2, CHRM3, NOS3, NOS2, EGF, PRKCB, TACR2, PTGFR, PTGER3, EGFR, PRKCA, PTGER1, MET, ADORA2A, KDR, FGFR2, NTRK1, PDGFRB, CCKBR, TBXA2R, FLT1, PDGFRA, FGFR1, P2RX3, EDNRA, HTR2A, HTR2C, CD38, F2R, GRM5, AGTR1, HTR6, HRH1, HRH2, OXTR | 41/327 |
| hsa05163 | 人巨细胞病毒感染 Human cytomegalovirus infection | CALM1, CASP3, CDK4, CCND1, GSK3B, MAPK1, MAPK14, PTGS2, PRKCB, RELA, TNFRSF1A, MDM2, PTGER3, EGFR, CCR1, PRKCA, PTGER1, MTOR, TNF-α, IKBKB, CHUK, SRC, CDK6, PTGER2, CCR3, JAK1, NFKBIA, PIK3CD, PIK3CB, PIK3CA, PDGFRA, MAP2K1, MAPK11, CXCR2, CASP8, PTGER4, IL6, MAPK3, ROCK2, ROCK1 | 40/327 |
图5
图5
冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化靶点的KEGG富集图
A:前20条信号通路气泡图;B:化合物-关键通路-靶点网络分析
Fig. 5
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.
A: Bubble chart of the top 20 signaling pathways; B: The compounds-key pathways-targets network analysis.
前20个信号途径通过化合物关键途径靶点分析网络进行分析,包括21个化合物和194个靶点(图5B)。金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、酒渣碱、花生四烯酸、11,14-二十碳二烯酸分别对应于51、50、39、30和28个靶点。PIK3CA、PIK3CB、PIK3CD、MAPK1、MAPK3和RELA分别对应17、17、17、16、16和15个信号通路。结果提示冬虫夏草可能通过多成分、多靶点、多途径抑制肾纤维化。
2.6 分子对接分析
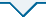
表3 分子对接结果
Table 3
| 成分 Compounds | MAPK1 (6SLG) | MAPK3 (2ZOQ) | PIK3CA (6OAC) | PIK3CB (4BFR) | PIK3CD (5T8F) | RELA (1VJ7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 金色酰胺醇酯Aurantiamide acetate | -5.296 | -5.744 | -4.536 | -8.860 | -5.161 | -5.095 |
| 啤酒甾醇Cerevisterol | -4.861 | -4.042 | -3.514 | -5.135 | -5.892 | -3.084 |
| 酒渣碱Flazin | -6.969 | -7.181 | -6.336 | -6.671 | -7.224 | -5.095 |
| 花生四烯酸Arachidonic acid | -3.999 | -3.406 | -4.431 | -6.135 | -5.877 | -3.754 |
| 11,14-二十碳二烯酸11,14-Eicosadienoic acid | -3.691 | -2.309 | -3.856 | -5.499 | -4.568 | -1.646 |
图6
图6
冬虫夏草活性成分与靶点的分子对接图
A:金色酰胺醇酯-PIK3CB;B:啤酒甾醇-PIK3CD;C:酒渣碱-PIK3CD;D:花生四烯酸-PIK3CB;E:11,14-二十碳二烯酸-PIK3CB
Fig. 6
Molecular docking diagram of active compounds in Chinese cordyceps and targets.
A: Aurantiamide acetate-PIK3CB; B: Cerevisterol-PIK3CD; C: Flazin-PIK3CD; D: Arachidonic acid-PIK3CB; E: 11,14-Eicosadienoic acid-PIK3CB.
3 讨论
慢性肾脏病已成为全球公共卫生问题,全世界8%-16%的人口患有慢性肾脏病(经铃等 2017;Kamyar & Denis 2017)。慢性肾病可导致肾纤维化,是肾组织(包括肾小球、肾小管、血管和间质)在各种损伤情况下持续协调反应的形态学表达(Black et al. 2019)。目前慢性肾病的研究热点主要集中在探讨肾纤维化的分子机制以及如何干预肾纤维化,应用血管紧张素转换酶抑制剂和血管紧张素Ⅱ受体阻滞剂治疗肾纤维化(Srivastava et al. 2020)。但通过某种化合物对特定靶点的干预很难控制肾纤维化的进展,很难达到理想的临床疗效。中医药以其多成分、多靶点、多途径的生物活性成分被认为是慢性肾病的重要治疗手段(Wang et al. 2017;时蔡林和张微 2021)。
冬虫夏草在肾病治疗方向一直都有临床应用,冬虫夏草联合聚精丸可有效改善男性不育症患者的精子质量,降低精子DNA碎片指数,提高聚精丸的补肾法疗效(杨朝旭等2021),冬虫夏草菌粉Hirsutella sinensis作为肾移植术后新型免疫抑制剂,降低环孢霉素引起肝毒性和肾毒性的发生率等不良反应(Li et al. 2009),虫草补肾胶囊通过调节细胞因子和抑制炎症反应,减缓糖尿病肾病患者肾纤维化的进程(谢秋芳等 2021)。
在化学成分-靶点的网络分析中,金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、酒渣碱、花生四烯酸、11,14-二十碳二烯酸是冬虫夏草抑制肾纤维化的主要活性成分,IL-6、TNF-α、MAPK3、EGFR和MAPK1是其主要靶点。通过查文献可知,11,14-二十碳二烯酸在冬虫夏草中相对含量为0.01%-0.18%(Guo et al. 2012),而金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、酒渣碱、花生四烯酸的含量尚未有文献报道,未来可进一步开展这些成分的化学分析研究,以提升药材的质量评价水平。金色酰胺醇酯和花生四烯酸为冬虫夏草特征抗肾纤维化成分,未曾在其他药用真菌(蛹虫草、灵芝、猪苓和茯苓)中报道;酒渣碱、啤酒甾醇和11,14-二十碳二烯在其他药用真菌(如蛹虫草、猪苓)中也有报道。已有研究报道金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、11,14-二十碳二烯有抗纤维化作用(Fan et al. 2020;张怡萍等 2020;Zhu et al. 2020),花生四烯酸可通过细胞色素P450环氧酶代谢成类花生酸类成分,保护肾病患者的肾功能,减缓肾纤维化进程(李莎莎2014)。IL-6是临床干预调节先天性和适应性免疫反应的主要靶点,在纤维化过程中,单侧输尿管闭塞小鼠肾脏IL-6受体水平升高;IL-6反式信号阻断可降低炎症、免疫细胞浸润和肾组织成纤维细胞的积聚(Jones et al. 2015;Chen et al. 2019)。TNF-α是一种多方向的促炎性细胞因子,主要由单核巨噬细胞分泌,导致多种形式的肾脏损伤。Wen et al.(2020)发现T淋巴细胞通过抑制Th17淋巴细胞表达和细胞反应产生TNF-α,减轻了肾毒性肾炎所致肾纤维化的作用。Nagae et al.(2008)发现,MAPK1/MAPK3磷酸化在诱导间质细胞增殖中起核心作用,发现肾上腺髓质素通过阻断MAPK1/MAPK3磷酸对肾纤维化有抑制作用。EGFR是一种具有酪氨酸激酶活性的跨膜受体,在肾上皮细胞和肾间质成纤维细胞中表达。Tang et al.(2013)发现,持续的EGFR激活可诱导肾成纤维细胞的活化和增殖,最终导致肾纤维形成。
KEGG通路富集分析表明,冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化的主要靶点是神经活性配体-受体相互作用、PI3K-Akt信号通路和钙信号通路,它们与神经功能、糖代谢和钙调节有关。冬虫夏草有61个基因参与神经活性配体-受体通路调节,虽然神经活性配体-受体通路不是直接调节肾纤维化,通过调节质膜上的神经受体和配体的相互作用,调节肾细胞代谢、自主神经功能和电生理活动等神经功能影响肾功能,从而抑制肾纤维化产生和发展。糖尿病肾病是糖尿病最常见、最严重的并发症,发展为肾纤维化,PI3K-Akt信号通路在糖代谢调控中起重要作用。PI3K-Akt信号通路与56个靶点相关,包括EGFR、IL-6、MAPK1、MAPK3、PIK3CA、PIK3CB、PIK3CD和RELA。Hu et al.(2021)发现,microRNA-29b通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路预防肾纤维化。Ca2+在肾纤维化的发展过程中起着重要的作用。钙信号通路涉及41个靶点,包括EGFR、EGF等。Mai et al.(2016)发现阻断Ca2+通道可以保护肾脏免受纤维化损伤。通过对前20条目的信号通路做网络药理学分析,发现PIK3CA、PIK3CB、PIK3CD、MAPK1、MAPK3和RELA靶点为冬虫夏草防治肾纤维化的关键靶点。PIK3CA、PIK3CB、PIK3CD是经典的IA PI3K簇,是纤维化研究的重要亚型。PIK3CA细胞生长的主调节因子,Shyamasundar et al.(2018)研究miR-128调控PIK3CA等靶点来抑制小鼠肾纤维化。Zhou et al.(2018)发现增加PIK3CD转录水平来介导AKT激活,抑制肾纤维化进程。RELA是NF-κB家族的重要蛋白靶点,经过翻译后修饰调控NF-κB通路的活性,并对炎症、代谢、肿瘤以及免疫应答进行调控,其调控失常易诱发多种恶性疾病发生,RELA/p65的抑制可以抑制炎症过程、降低成纤维细胞的增殖,从而降低肌腱粘连形成(陈帅2017)。从通路-靶点-成分网络分析可知冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化的20条潜在信号通路不是相互独立的,而是相互交叉、相互影响的,这与中医治疗疾病的整体理念一致。
若结合能≤0,蛋白分子与小分子能自发地结合,结合能≤-5.0表明有较好的结合活性,结合能≤-7.0表明具有强烈的结合活性(许嘉慧等 2021)。分子对接结果表明冬虫夏草的活性成分金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、酒渣碱、花生四烯酸、11,14-二十碳二烯酸与关键靶点PIK3CA、PIK3CB、PIK3CD、MAPK1、MAPK3和RELA均有自发的结合。金色酰胺醇酯与PIK3CB的结合最好,其结合能为-8.860KJ/mol;酒渣碱与这6个关键靶点均有较好的结合,与MAPK3、PIK3CD靶点强烈结合,其结合能分别为-7.181、-7.224kJ/mol;11,14-二十碳二烯酸与其他4个活性成分相比,与这6个关键靶点的结合能力稍差些,与PIK3CB有较好的结合,其结合能为-5.499KJ/mol。分子对接结果表明冬虫夏草活性成分与主要靶点结合性均较好,能减缓肾纤维化进程。
综上所述,通过网络药理学方法对冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化的主要活性成分、核心靶基因和关键信号通路进行了筛选,共发现22种生物活性化合物,其中以金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、花生四烯酸、酒渣碱和11,14-二十碳二烯酸为主要活性成分;共关联364个关键靶基因,发现163条信号通路,其中神经活性配体-受体相互作用、PI3K-Akt信号通路、钙信号通路和人巨细胞病毒感染是关键通路;分子对接结果显示冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化过程中,其核心化合物金色酰胺醇酯、啤酒甾醇、酒渣碱、花生四烯酸、11,14-二十碳二烯酸与PIK3CA、PIK3CB、PIK3CD、MAPK1、MAPK3、RELA具有良好的结合性能。本研究从网络药理学和分子对接的角度探讨了冬虫夏草治疗肾纤维化的作用机制,结果表明冬虫夏草通过多组分、多靶点、多途径减缓肾纤维化过程,研究结果为冬虫夏草在临床肾病的使用提供了科学参考。
参考文献
Recent advances in the analysis of nucleosides in Chinese cordyceps
Renal inflammation and fibrosis: a double-edged sword
DOI:10.1369/0022155419852932 URL [本文引用: 1]
The effect and associated mechanism of RelA/p65 in tendon adhesion formation
Blocking interleukin-6 trans-signaling protects against renal fibrosis by suppressing STAT3 activation
DOI:10.7150/thno.32352
PMID:31281526
[本文引用: 1]

: Renal fibrosis is the terminal manifestation of chronic and irreversible renal disease. Effective therapies other than dialysis are extremely limited. In this study, we investigated the potential effects of targeting elevated interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in the treatment of renal fibrosis. : Fc-gp130 was used to specifically block IL-6 trans-signaling. Unilateral ureteral occlusion (UUO) and ischemia reperfusion (IR) mouse models were constructed to investigate the therapeutic effect of Fc-gp130 on renal fibrosis. The role of IL-6 trans-signaling and phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 in regulating fibroblast accumulation and extracellular matrix protein deposition were evaluated in cell experiments and mouse models. : The kidneys of mice with UUO were found to have elevated soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R) levels in the progression of fibrosis. Fc-gp130 attenuated renal fibrosis in mice, as evidenced by reductions in tubular atrophy and the production of extracellular matrix protein. Blockade of IL-6 trans-signaling with Fc-gp130 also reduced inflammation levels, immune cell infiltration, and profibrotic cytokines expression in renal tissue, with decreased STAT3 phosphorylation and reduced fibroblast accumulation in the renal tissue. In vitro, Fc-gp130 also reduced the phosphorylation of STAT3 induced by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 in fibroblasts. Furthermore, the therapeutic effect of Fc-gp130 was confirmed in a model of acute kidney injury-chronic kidney disease. : Overall, IL-6 trans-signaling may contribute to crucial events in the development of renal fibrosis, and the targeting of IL-6 trans-signaling by Fc-gp130 may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of renal fibrosis.
Cordyceps sinensis attenuates renal fibrosis and suppresses BAG3 induction in obstructed rat kidney
A network pharmacology approach to explore the mechanisms of shuganjianpi formula in liver fibrosis
Network pharmacology study on prevention and treatment of novel coronavirus pneumonia by FangwenJiuweiyin
Fatty acid composition of lipids in wild Cordyceps sinensis from major habitats in China
MicroRNA-29b prevents renal fibrosis by attenuating renal tubular epithelial cell- mesenchymal transition through targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway
Antiaging effect of Cordyceps sinensis extract
DOI:10.1002/ptr.2576 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research progress of depression in patients with chronic kidney disease
Interleukin-6 in renal disease and therapy
DOI:10.1093/ndt/gfu233 URL [本文引用: 1]
Nutritional management of chronic kidney disease
DOI:10.1056/NEJMra1700312 URL [本文引用: 1]
HPLC fingerprint analysis of Cordyceps sinensis by ionic liquid-assisted extraction
Extracts of Cordyceps sinensis inhibit breast cancer growth through promoting M1 macrophage polarization via NF-κB pathway activation
DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2020.112969 URL [本文引用: 1]
Metabonomic research of the effect of Zhen Wu decoction on renal fibrosis rat
Clinical application of Cordyceps sinensis on immunosuppressive therapy in renal transplantation
Mechanism of Codonopsispilosula in the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis based on network pharmacology
Blockade of orai1 store-operated calcium entry protects against renal fibrosis
DOI:10.1681/ASN.2015080889 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research and application of fresh Cordyceps sinensis
Adrenomedullin inhibits connective tissue growth factor expression, extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and renal fibrosis
DOI:10.1038/ki.2008.98
PMID:18401334
[本文引用: 1]

Systemic administration of the potent vasodilating peptide adrenomedullin reduces cardiac and renal fibrosis in hypertensive animals. Here, we investigated the effects of kidney-specific adrenomedullin gene delivery in normotensive rats after unilateral ureteral obstruction, an established model of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Overexpression of exogenous adrenomedullin in the renal interstitium following ureteral obstruction significantly prevented fibrosis and proliferation of tubular and interstitial cells. In this model, there is upregulation of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) mRNA expression and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation, and adrenomedullin overexpression suppressed both of these activities without altering the blood pressure. In NRK-49F renal fibroblasts, adrenomedullin reduced transforming growth factor-beta-induced CTGF and fibronectin mRNA upregulation through the cyclic AMP/protein kinase A signaling pathway, and suppressed ERK phosphorylation and cell proliferation. In the kidneys with an obstructed ureter, adrenomedullin receptor gene expression was upregulated along with cyclic AMP production in kidney slices. The latter effect was partially blocked by a neutralizing antibody to adrenomedullin, indicating that an endogenous peptide-receptor system was activated. Our results show that overexpression of exogenous adrenomedullin in the ureteral-obstructed kidney prevents tubulointerstitial fibrosis and cell proliferation through the cyclic AMP-mediated decrease of CTGF induction and ERK phosphorylation.
Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signal pathway is involved in the effect of Cordyceps sinensis against renal fibrosis in 5/6 nephrectomy rats
DOI:10.1016/j.fct.2013.04.037 URL [本文引用: 1]
Research progress on prevention and treatment of renal interstitial fibrosis with single Chinese medicine
Study on the mechanism of Cordyceps sinensis in treating membranous nephropathy based on network pharmacology
Analysis of chemical compounds in Chinese cordyceps
Content analyses of three kinds of sterols in different development stages of Chinese cordyceps
Pharmaceutical and clinical research progress on Chinese cordyceps and related products against respiratory inflammatory diseases
Clinical study on Shenshuaining capsule combined with high colon dialysis in the treatment of 2-3 stage chronic nephropathy
miR-128 regulates genes associated with inflammation and fibrosis of rat kidney cells in vitro
DOI:10.1002/ar.23763
PMID:29278451
[本文引用: 1]

microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate diverse cellular functions and signaling pathways via inhibiting the expression of their target genes. Given that miR-128 mediates mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and production of reactive oxygen species and pro-inflammatory chemokines in various types of cells and tissues, and that miR-128 is differentially expressed in aged and diseased kidneys, we hypothesized that miR-128 may play key roles in kidney inflammation. Hence, in this study, we evaluated the biological effects of miR-128 in normal rat kidney (NRK) cells in vitro. Our results revealed that overexpression of miR-128 enhanced expression of genes associated with inflammation, pro-inflammatory cytokines and fibrosis in NRK cells. The recent reports showing that expression of miR-128 is increased in liver and lung fibrosis, together with the findings in this study, suggest that miR-128 may be a pro-fibrotic miRNA that regulates fibrosis in various tissues. Anat Rec, 301:913-921, 2018. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme ameliorates renal fibrosis by mitigating DPP-4 level and restoring antifibrotic microRNAs
DOI:10.3390/genes11020211 URL [本文引用: 1]
Sustained activation of EGFR triggers renal fibrogenesis after acute kidney injury
DOI:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.04.005 URL [本文引用: 1]
Artificially cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis alleviates diabetic nephropathy and its podocyte injury via inhibiting P2X7R expression and NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Niaoduqing granules relieve chronic kidney disease symptoms by decreasing renal fibrosis and anemia
DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.18473
PMID:28915563
[本文引用: 1]

NiaoDuQing (NDQ) granules, a traditional Chinese medicine, has been clinically used in China for over fourteen years to treat chronic kidney disease (CKD). To elucidate the mechanisms underlying the therapeutic benefits of NDQ, we designed an approach incorporating chemoinformatics, bioinformatics, network biology methods, and cellular and molecular biology experiments. A total of 182 active compounds were identified in NDQ granules, and 397 putative targets associated with different diseases were derived through ADME modelling and target prediction tools. Protein-protein interaction networks of CKD-related and putative NDQ targets were constructed, and 219 candidate targets were identified based on topological features. Pathway enrichment analysis showed that the candidate targets were mostly related to the TGF-β, the p38MAPK, and the erythropoietin (EPO) receptor signaling pathways, which are known contributors to renal fibrosis and/or renal anemia. A rat model of CKD was established to validate the drug-target mechanisms predicted by the systems pharmacology analysis. Experimental results confirmed that NDQ granules exerted therapeutic effects on CKD and its comorbidities, including renal anemia, mainly by modulating the TGF-β and EPO signaling pathways. Thus, the pharmacological actions of NDQ on CKD symptoms correlated well with predictions.
Chronic kidney disease
DOI:S0140-6736(16)32064-5
PMID:27887750
[本文引用: 1]

The definition and classification of chronic kidney disease (CKD) have evolved over time, but current international guidelines define this condition as decreased kidney function shown by glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of less than 60 mL/min per 1·73 m, or markers of kidney damage, or both, of at least 3 months duration, regardless of the underlying cause. Diabetes and hypertension are the main causes of CKD in all high-income and middle-income countries, and also in many low-income countries. Incidence, prevalence, and progression of CKD also vary within countries by ethnicity and social determinants of health, possibly through epigenetic influence. Many people are asymptomatic or have non-specific symptoms such as lethargy, itch, or loss of appetite. Diagnosis is commonly made after chance findings from screening tests (urinary dipstick or blood tests), or when symptoms become severe. The best available indicator of overall kidney function is GFR, which is measured either via exogenous markers (eg, DTPA, iohexol), or estimated using equations. Presence of proteinuria is associated with increased risk of progression of CKD and death. Kidney biopsy samples can show definitive evidence of CKD, through common changes such as glomerular sclerosis, tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis. Complications include anaemia due to reduced production of erythropoietin by the kidney; reduced red blood cell survival and iron deficiency; and mineral bone disease caused by disturbed vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate metabolism. People with CKD are five to ten times more likely to die prematurely than they are to progress to end stage kidney disease. This increased risk of death rises exponentially as kidney function worsens and is largely attributable to death from cardiovascular disease, although cancer incidence and mortality are also increased. Health-related quality of life is substantially lower for people with CKD than for the general population, and falls as GFR declines. Interventions targeting specific symptoms, or aimed at supporting educational or lifestyle considerations, make a positive difference to people living with CKD. Inequity in access to services for this disease disproportionally affects disadvantaged populations, and health service provision to incentivise early intervention over provision of care only for advanced CKD is still evolving in many countries.Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
TNF-α in T lymphocytes attenuates renal injury and fibrosis during nephrotoxic nephritis
DOI:10.1152/ajprenal.00347.2019 URL [本文引用: 1]
Cordyceps sinensis may inhibit Th22 cell chemotaxis to improve kidney function in lgA nephropathy
Effect of ChongcaoBushen capsules in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy patients with deficiency of both qi and yin type
Mechanism analysis of astragali radix in treatment of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking method
Anti-inflammatory principles from Cordyceps sinensis
DOI:10.1021/np100902f URL [本文引用: 1]
Cordyceps sinensis combined with Jujing pills for male infertility
Ophiocordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris: research advances, issues and perspectives
Mycobiotal investigation of natural Ophiocordyceps sinensis based on culture- dependent investigation
Pharmacodynamic material basis and molecular mechanism of Zhenwudecoction in treatment of renal fibrosis by network pharmacology
Progress on pharmaceutical effects of natural Cordyceps sinensis and fermentative cordycepic fungal powder in recent five years
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) promotes TGF-β-induced renal tubular epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and renal fibrosis through the PI3K subunit p110δ
DOI:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.04.023 URL [本文引用: 1]
Elucidating the mechanisms of Huganbuzure granule in the treatment of liver fibrosis via network pharmacology
基于网络药理学和分子对接法探讨黄芪治疗桥本甲状腺炎的机制