灵芝Ganoderma lingzhi Sheng H. Wu, Y. Cao & Y.C. Dai(Cao et al. 2012)隶属多孔菌科灵芝属(Cui et al. 2019),是我国传统的珍贵中药材,素有“仙草”、“瑞草”之称,具有补气安神、止咳平喘、延年益寿等功效(戴玉成等2013;林志彬 2015)。三萜类化合物是灵芝的主要活性成分之一,具有抗肿瘤(杜国华等 2017;谭洪升等 2018;Wu et al. 2019)、护肝(Liu et al. 2014;蔡蕤 2020)、抗炎(Su et al. 2020)、抗病毒(Shiv et al. 2019)、抑制前列腺增生(Liu et al. 2010)、抗动脉粥样硬化(Hsu et al. 2018)等多种良好且广泛的药理活性。因此,三萜是评价灵芝保健产品开发的重要指标成分。
目前,灵芝在国内大部分地区都实现了人工栽培。不同栽培地、不同品种的灵芝,其三萜成分的含量有较大差异(胡居吾 2006;李保明等 2012;谢宝靖等 2016;贾红岩等 2017;腾李铭等 2021)。在灵芝保健产品开发时,选取三萜含量高的子实体原料,将大大节省生产的成本。而在选择灵芝原料时,灵芝三萜检测方法的精确性将会影响结果的准确性。超高效液相色谱-三重四级杆质谱联用(ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopy,UPLC-MS/MS)将液相色谱高分离度的优点与质谱检测器高选择性和高灵敏度的优点结合起来,分析特异性强、定量结果可靠。利用该技术建立的灵芝三萜检测方法,比以往单纯用高效液相色谱检测灵芝三萜化合物更加精准(Da et al. 2012)。
灵芝三萜的提取方法主要包括热回流提取、超声提取、超临界CO2提取、微波提取等(任奕 2020)。虽然超声提取、超临界CO2提取和微波提取各有优势,但在工业化生产时,大多数企业还是选择了操作简单、设备通用性强的溶剂热回流提取方式。热回流提取利用溶剂加热后冷凝回流,使三萜连续不断地被溶剂提取。此外加热有利于溶剂分子的热运动,可加速三萜物质的溶出,从而提高三萜的提取效率。考虑到工业生产需要衡量经济成本,有必要优化热回流提取工艺以找到既能有效提取灵芝三萜又能节约成本的条件。天然产物提取时,常用的工艺优化方法有正交法(刘盛荣等 2019)、均匀设计法(段晓颖等 2018)、响应面法(高文庚等 2019)等,其中响应面法(response surface methodology,RSM)通过建立多元二次回归数学模型,连续对实验的各个水平进行分析,结合响应面交互作用,可以得到更为具体准确的最佳工艺(Chin et al. 2009)。
本研究基于UPLC-MS/MS定量检测法,以提取物得率和测得的灵芝中的三萜含量为考察指标,旨在寻找三萜含量较高的子实体原料,通过单因素和响应面实验优化热回流提取灵芝三萜的工艺,并采用最佳工艺进行实验室和中试放大验证,其结果可为灵芝三萜的工业提取提供理论依据,为灵芝产品的开发利用奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 供试材料
1.1.1 实验材料和试剂:sd-1、sd-2、sd-3、sd-4收集自山东聊城冠县、sh-1为沪农灵芝1号、hn-1为海南儋州菌草灵芝、zj-1为浙江龙泉龙芝2号,经上海市农业科学院食用菌研究所唐传红副研究员鉴定,均为赤芝Ganoderma lingzhi。三萜标准品:灵芝酸I、灵芝烯酸C、灵芝酸C2、灵芝酸C6、灵芝酸G、灵芝烯酸B、灵芝酸B、灵芝烯酸A、灵芝酸K、灵芝酸A、灵芝酸H、赤芝酸A、灵芝酸N、灵芝烯酸H、3-O-acetyl-16α-hydroxytrametenolic acid、灵芝烯酸D、灵芝酸D、灵芝酸F、灵芝酸DM,购自武汉天植生物技术有限公司,纯度均大于98%。无水乙醇、冰醋酸(分析纯,国药集团药业股份有限公司);乙腈、甲醇、异丙醇(质谱级,德国Merck公司)。
1.1.2 仪器:中试提取机组为50L提取罐(武汉市立中医药装备制造有限公司)和WDRO 034-0.7(HX-24D-1)型全自动加热蒸汽锅炉(上海华征特种锅炉制造有限公司);TDP-400型强力破碎机(天津市渤海鑫茂制药设备有限公司);TCS-150电子台秤(永康市太阳横器有限公司);MS-3002TS电子天平[梅特勒-托利多(上海)有限公司];Büchi Vac V-700旋转蒸发仪(瑞士Büchi公司);SXKW数显控温加热套(北京市永光明医疗仪器有限公司);SHB-IIIG型循环水式真空泵(郑州长城科工贸有限公司);NL TRA超纯水仪(ELGA LabWater公司);Agilent 1290-6495液质联用仪(美国Agilent公司)。
1.2 三萜检测方法和标准曲线的建立
三萜含量检测采用超高效液相-三重四级杆质谱联用(UPLC-MS/MS)分析方法(郑洁 2019)。色谱条件:色谱柱Agilent Eclipse C18(2.1mm×100mm,1.8μm),流动相为乙腈(A)-0.01%冰醋酸水溶液(B),梯度洗脱(0-10min,A:26%-27%;10-23min,A:27%-37%;23-26min,A:37%-60%;26-36min,A:60%-90%;36-41min,A:90%-100%),流速0.4mL/min,柱温30℃,进样量2μL,检测波长254nm。质谱条件:电喷雾离子源(AJS-ESI),扫描方式为负离子模式,动态多反应监控(DMRM),干燥气(氮气)温度200℃,干燥气流速14.0L/min,鞘气(氮气)温度300℃,鞘气流速11.0L/min,喷雾器压力25psi,毛细管电压3 000V,喷嘴电压1 500V,碰撞电压380V。
标准品的配置和检测:分别准确称取各标准品制备成浓度均为500ng/mL的混合标准溶液;用甲醇将混合标准溶液逐级稀释为200、100、50、25ng/mL。按以上液相和质谱条件检测系列混合标准溶液,以标准品溶液浓度X(ng/mL)为横坐标,峰面积Y为纵坐标得到三萜类化合物的标准曲线,根据3倍的S/N计算检出限(LOD),10倍的S/N计算定量限(LOQ)。
1.3 灵芝原料的分析
准确称取粉碎的sd-1、sd-2、sd-3、sd-4、sh-1、hn-1、zj-1灵芝子实体各5g,按20:1的液料比加入无水乙醇超声1h,取1mL溶液过0.22μm滤膜,按1.2方法上样分析,并计算三萜含量。
1.4 单因素实验
分别考察乙醇浓度、提取时间、提取次数、液料比等因素对热回流提取灵芝三萜的影响。
1.4.1 乙醇浓度:称取50g灵芝样品置于2L圆底烧瓶中,按12:1(g/mL,下同)的液料比分别加入60%、70%、80%、90%和100%乙醇,加热套加热回流提取2h,实验3组平行,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率。
1.4.2 提取时间:称取50g灵芝样品置于2L圆底烧瓶中,按12:1的液料比加入80%乙醇,加热套分别加热回流提取1、2、3h,实验3组平行,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率。
1.4.3 提取次数:称取50g灵芝样品置于2L圆底烧瓶中,分别按12:1的液料比加入80%乙醇,加热套加热回流提取2h,分别提取1次、2次、3次,实验3组平行,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率。
1.4.4 液料比:提取1次的不同液料比:称取50g灵芝样品置于2L圆底烧瓶中,分别按8:1、10:1、12:1、15:1的液料比加入80%乙醇,加热套加热回流提取2h,实验3组平行;提取2次的不同液料比:称取50g灵芝样品置于2L圆底烧瓶中,分别按10:1、12:1、15:1的液料比加入80%乙醇,加热套加热回流提取2h,提取重复2次,实验设3组平行,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率。
1.5 响应面实验
在单因素实验的基础上,选取乙醇浓度(A)、液料比(B)、提取时间(C)3个因素,以测得的灵芝三萜含量(D)和提取物得率(E)为响应值,采用Design Expert-12.0软件进行Box-Behnken组合设计实验方案,并以-1、0、1分别代表变量的因素编码,进行加热套加热回流提取灵芝三萜交互条件的优化,各进行3组平行实验,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率,并用软件进行模型构建及分析。变量的因素编码及水平见表1。
表1 响应面分析实验因素水平表
Table 1
| 因素 Factor | 水平Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |
| A乙醇浓度 Ethanol concentration (%) | 70 | 80 | 90 |
| B液料比 Liquid to solid ratio (g/mL) | 10:1 | 12:1 | 14:1 |
| C提取时间 Extraction time (h) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
1.6 最佳提取工艺验证实验
1.6.1 响应面优化最佳工艺验证:称取50g灵芝样品置于2L圆底烧瓶中,按响应面优化得到的最佳工艺用加热套回流提取一次,实验设3组平行,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率。
1.6.2 最终优化工艺验证:称取50g灵芝样品置于2L圆底烧瓶中,按响应面优化得到的最佳工艺用加热套重复回流提取2次,实验设3组平行,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率。
1.6.3 中试放大验证:称取3kg灵芝样品置于50L提取罐中,按响应面优化得到的最佳工艺用中试设备重复回流提取2次,按1.2方法进样分析并计算三萜含量及提取物得率。
1.7 样品处理及三萜含量和提取物得率计算
准确称取粉碎的灵芝样品按设计进行实验,得到的提取液过滤后定容至一定体积,混匀后吸取1mL稀释一定倍数后按1.2方法进样分析,剩余溶液旋干称重,按公式(1)、(2)分别计算三萜含量及提取物得率,取平均值。
式(1)中X为三萜含量(mg/g),Xi为19个三萜化合物的进样含量(ng/mL),n为稀释倍数,V为定容体积(mL),M为灵芝子实体重量(g),m为提取物重量(g)。
2 结果与分析
2.1 灵芝三萜UPLC-MS/MS法的建立
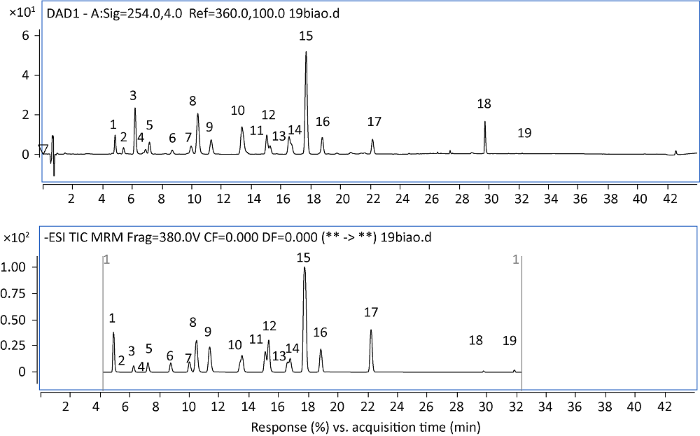
图1
图1
灵芝三萜标准品超高效液相色谱图和总离子流图
1:灵芝酸I;2:灵芝烯酸C;3:灵芝酸C2;4:灵芝酸C6;5:灵芝酸G;6:灵芝烯酸B;7:灵芝酸B;8:灵芝烯酸A;9:灵芝酸K;10:灵芝酸A;11:灵芝酸H;12:赤芝酸A;13:灵芝酸N;14:灵芝烯酸H;15:灵芝烯酸D;16:灵芝酸D;17:灵芝酸F;18:灵芝酸DM;19:3-O-acetyl-16α-hydroxytra-metenolic acid. 下同
Fig. 1
UPLC and TIC graph of Ganoderma lingzhi triterpenoid standard.
1: Ganoderic acid I; 2: Ganoderenic acid C; 3: Ganoderic acid C2; 4: Ganoderic acid C6; 5: Ganoderic acid G; 6: Ganoderenic acid B; 7: Ganoderic acid B; 8: Ganoderenic acid A; 9: Ganoderic acid K; 10: Ganoderic acid A; 11: Ganoderic acid H; 12: Lucidenic acid A; 13: Ganoderic acid N; 14: Ganoderenic acid H; 15: Ganoderenic acid D; 16: Ganoderic acid D; 17: Ganoderic acid F; 18: Ganoderic acid DM; 19: 3-O-acetyl-16α-hydroxytra-metenolic acid. The same below.
表2 三萜标准品的线性回归方程及检测限、定量限
Table 2
| 三萜标准品 Triterpenoid standard | 回归方程 Regressive equations | R2 | 检测限 LOD (ng) | 定量限 LOQ (ng) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganoderic acid I | Y=8.735×102X-8.725×103 | 0.9969 | 1.52 | 4.37 |
| Ganoderenic acid C | Y=7.865×10X-6.482×102 | 0.9965 | 1.14 | 3.76 |
| Ganoderic acid C2 | Y=1.518×102X-1.831×103 | 0.9968 | 2.11 | 6.31 |
| Ganoderic acid C6 | Y=3.359×103X-3.753×103 | 0.9975 | 1.46 | 4.38 |
| Ganoderic acid G | Y=3.417×102X-3.997×103 | 0.9974 | 1.04 | 3.24 |
| Ganoderenic acid B | Y=1.201×103X-1.742×104 | 0.9975 | 1.77 | 5.46 |
| Ganoderic acid B | Y=1.098×103X-1.521×104 | 0.9977 | 1.04 | 5.39 |
| Ganoderenic acid A | Y=1.175×102X-9.416×104 | 0.9967 | 1.27 | 4.86 |
| Ganoderic acid K | Y=6.971×102X-8.832×103 | 0.9971 | 2.01 | 3.94 |
| Ganoderic acid A | Y=4.668×102X-5.997×103 | 0.9969 | 2.16 | 5.36 |
| Ganoderic acid H | Y=9.463×102X-1.157×104 | 0.9968 | 1.52 | 4.95 |
| Lucidenic acid A | Y=3.006×102X-2.821×103 | 0.9968 | 1.09 | 6.06 |
| Ganoderic acid N | Y=5.227×102X-6.549×103 | 0.9970 | 1.27 | 4.65 |
| Ganoderenic acid H | Y=3.953×103X-5.466×104 | 0.9966 | 1.31 | 4.97 |
| Ganoderenic acid D | Y=3.466×103X-4.006×104 | 0.9967 | 1.05 | 5.28 |
| Ganoderic acid D | Y=8.780×102X-9.416×103 | 0.9966 | 1.12 | 6.05 |
| Ganoderic acid F | Y=1.551×103X-2.154×104 | 0.9966 | 1.03 | 4.93 |
| Ganoderic acid DM | Y=2.084×10X-1.095×102 | 0.9957 | 1.37 | 5.96 |
| O-acetyl-16α-hydroxytra- metenolic acid | Y=2.801×10X-3.339×102 | 0.9956 | 1.24 | 5.27 |
表3 不同灵芝子实体的三萜含量对比
Table 3
| 灵芝样品 Ganoderma sample | sd-1 | sd-2 | sd-3 | sd-4 | sh-1 | hn-1 | zj-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三萜含量 Triterpenoid concentration (mg/g) | 6.3330 | 8.8926 | 4.0318 | 6.6580 | 8.0521 | 7.9151 | 6.9516 |
图2
2.2 三萜提取的单因素实验
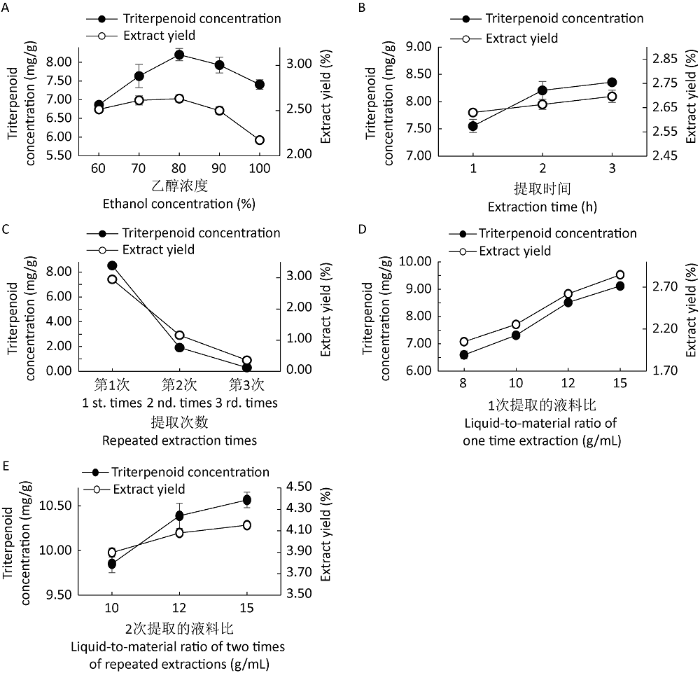
2.2.1 乙醇浓度对三萜提取的影响:随着乙醇浓度的增加,三萜含量和提取物得率均呈现先上升后下降的趋势(图3A),在乙醇浓度为80%时,三萜含量和提取得率均为最高,分别为8.2062mg/g和2.63%。因此,选取80%乙醇浓度作为最佳提取用浓度。
图3
图3
不同因素对灵芝子实体三萜提取的影响
A:乙醇浓度;B:提取时间;C:提取次数;D:一次提取的液料比;E:2次提取的液料比
Fig. 3
Effects of different factors on the co-extraction of triterpenoids in the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma lingzhi.
A: Ethanol concentration; B: Extraction time; C: Extraction frequency; D: The liquid-to-material ratio of one time extraction; E: The liquid-to-material ratio of two times of repeated extractions.
2.2.2 提取时间对三萜提取的影响:在实验范围内,随着提取时间的增加,三萜含量和提取物得率逐渐升高(图3B)。三萜含量在3h时最高,为8.3552mg/g。显著性分析发现,提取2h时,三萜含量达到8.2062mg/g,与提取3h的三萜含量的差异并不显著(P>0.05);此外,分别提取2h和3h时,提取物得率之间的差异也不显著(P>0.05)。综合三萜含量、提取物得率以及生产能耗,选择提取的适宜时间为2h。
2.2.3 提取次数对三萜提取的影响:提取时,随着提取次数增加,每次得到的三萜含量和提取物得率会越来越低,因此寻找提取灵芝三萜的最佳提取次数对节约成本至关重要。样品第1次提取时三萜含量和提取物得率较高,分别为8.5207mg/g和2.95%;第2次提取时为1.9160mg/g和1.20%,而第3次仅提取到极少量的灵芝三萜(图3C),考虑到生产经济性,灵芝三萜提取次数以2次为宜。
2.2.4 液料比对三萜提取的影响:郑士彬等(2015)通过单因素实验发现液料比为15:1时灵芝三萜提取率最大,故本研究以液料比为15:1作为节点,以溶剂刚好浸没固体为最低比例,寻求既能最大程度提取灵芝三萜又能减少溶剂用量的经济高效的液料比。随着液料比的增大,三萜含量和提取物得率均呈现上升的趋势(图3D)。但液料比从10:1到12:1时三萜含量的增加趋势明显高于12:1到15:1时的趋势。由2.2.3结果可知,随着提取次数增加,三萜含量和提取物得率的值逐渐降低,两次便可将原料中的三萜尽可能提取出来,因而实验在此基础上又选取10:1、12:1、15:1的液料比重复提取两次进行测定。随着液料比的增大,三萜含量逐渐增加(图3E)。且液料比为15:1时三萜含量为10.5754mg/g,同液料比为12:1时的10.4367mg/g相比,差异并不显著(P>0.05)。另外液料比从10:1到15:1提取物得率基本稳定在4.10%左右,无显著变化。综合三萜含量和提取物得率及生产经济性,灵芝三萜提取液料比以12:1为宜。
2.3 三萜提取的响应面实验
2.3.1 响应面实验分析:单因素实验结果显示,乙醇体积浓度为80%、提取时间为2h、液料比为12:1时,既能最大程度提取灵芝中的三萜又能减少乙醇用量、节省时间,经济高效。以此作为较优水平进行响应面实验设计得到的实验结果见表4。
表4 响应面实验设计及结果
Table 4
| Run | Factor | Response | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: Ethanol concentration (%) | B: Liquid-to-material ratio (mL/g) | C: Extraction time (h) | D: Triterpenoid content (mg/g) | E: Extract yield (%) | |
| 1 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 7.6126 | 2.73 |
| 2 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 7.5185 | 2.46 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 8.6299 | 2.99 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.5524 | 2.81 |
| 5 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 7.9230 | 2.56 |
| 6 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 8.2636 | 2.91 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 7.4777 | 2.57 |
| 8 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 9.0285 | 3.06 |
| 9 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 8.6749 | 3.03 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.5795 | 2.84 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8.5660 | 2.79 |
| 12 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 7.1845 | 2.36 |
| 13 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7.9888 | 2.76 |
| 14 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7.6104 | 2.63 |
| 15 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 7.3054 | 2.47 |
2.3.2 模型方程的建立:根据表4的结果计算各项回归系数,以这些回归系数分别建立灵芝三萜含量(D)和提取物得率(E)与乙醇浓度(A)、液料比(B)、提取时间(C)3个因素的数学回归模型。可以得出二次回归方程式为:
D=8.5660-0.20A+0.5488B+0.1984C-0.1413AB-0.1296AC-0.0015BC-0.6557A2-0.218B2-0.1692C2;
E=2.8133-0.1025A+0.24875B+0.05125C-0.04AB-0.03AC-0.0075BC-0.1079A2-0.0504B2+0.0046C2;
在回归方程中,B、C变量的正系数表明,该变量的正向变化能引起响应值的增加;A变量负系数表明,该变量的正向变化会引起响应值的减少。负的二次项系数表明,方程的抛物面开口向下,具有极大值点,可进行最优条件分析。
2.3.3 显著性检验及响应面交互作用分析:响应面回归模型的方差分析见表5和表6,乙醇浓度(A)、液料比(B)、提取时间(C)两两交互作用的响应面图见图4和图5。响应面图底部为等高线图,等高线的形状反映交互效应的强弱大小,圆形表示两因素交互作用不显著,而椭圆形则表示两因素交互作用显著。构建的模型均极显著(P<0.0001),失拟项不显著P>0.05,说明模型合适;模型的校正决定系数R2Adj均大于0.95,说明该模型能较好地解释响应值的变化;模型的相关系数R2均大于0.95,说明该模型拟合程度良好,预测值与实测值之间有较好的相关性,实验误差小,可以用回归方程代替实验真实地对实验结果进行分析和预测。模型的一次项A、B、C影响均极显著,从F值可以看出,单因素对三萜含量和提取物得率的影响顺序均为B>A>C,即液料比>乙醇浓度>提取时间。三萜含量选用的模型中二次项A2、B2、C2影响极其显著。交互项AB影响显著,AC、BC影响不显著,该结论也可从图4得到验证。而提取物得率选用的模型中二次项A2影响极其显著、B2影响显著、C2影响不显著。交互项AB、AC影响极其显著,BC影响不显著,该结论也可从图5得到验证。
表5 以三萜含量为响应值的响应面回归模型的方差分析
Table 5
| Source | df | Mean square | F-value | P-value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 0.5383 | 3894.2208 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| A: Ethanol concentration | 1 | 0.3180 | 2300.9773 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| B: Liquid-to-material ratio | 1 | 2.4098 | 17434.2807 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| C: Extraction time | 1 | 0.3147 | 2277.0936 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| AB | 1 | 0.0799 | 577.7910 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| AC | 1 | 6.72E-02 | 485.8799 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| BC | 1 | 8.70E-06 | 0.0630 | 0.8119 | Not significant |
| A² | 1 | 1.5876 | 11486.2668 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| B² | 1 | 0.0548 | 396.5123 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| C² | 1 | 0.1056 | 764.3833 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| Residual | 5 | 0.0001 | |||
| Lack of fit | 3 | 0.0001 | 0.5880 | 0.6791 | Not significant |
| Pure error | 2 | 0.0002 | |||
| Cor total | 14 | ||||
| R²=0.9987 R²adj=0.9996 | |||||
表6 以提取物得率为响应值的响应面回归模型的方差分析
Table 6
| Source | df | Mean square | F-value | P-value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9 | 0.0734 | 124.8029 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| A: Ethanol concentration | 1 | 0.0841 | 142.8612 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| B: Liquid-to-material ratio | 1 | 0.4950 | 841.3810 | <0.001 | Very significant |
| C: Extraction time | 1 | 0.0210 | 35.7153 | 0.0019 | Very significant |
| AB | 1 | 0.0064 | 10.8782 | 0.0215 | Significant |
| AC | 1 | 0.0036 | 6.1190 | 0.0563 | Not significant |
| BC | 1 | 0.0002 | 0.3824 | 0.5634 | Not significant |
| A² | 1 | 0.0430 | 73.0889 | 0.0004 | Very significant |
| B² | 1 | 0.0094 | 15.9523 | 0.0104 | Significant |
| C² | 1 | 7.76E-05 | 0.1318 | 0.7314 | Not significant |
| Residual | 5 | 0.0006 | |||
| Lack of fit | 3 | 0.0006 | 0.8816 | 0.5703 | Not significant |
| Pure error | 2 | 0.0006 | |||
| Cor total | 14 | ||||
| R²=0.9553 R²adj=0.9876 | |||||
图4
图4
以三萜含量为响应值的3因素两两交互作用的响应面图
Fig. 4
Response surface graph of 3 factor pairwise interaction with triterpenoid content as response value.
图5
图5
以提取物得率为响应值的3因素两两交互作用的响应面图
Fig. 5
Response surface graph of the 3 factor pairwise interaction with the extract yield as the response value.
2.4 最佳提取工艺验证实验
响应面结果表明各因素对三萜含量和提取物得率的影响均不是简单的线性关系,且单独选用三萜含量或提取物得率作为考察指标优化的最佳工艺条件也有一定区别。为了得到尽可能多的高三萜含量的提取物,本研究在三萜含量和提取物得率均为最大的情况下,遵循尽可能节约成本的原则,得到的最优交互组合为:乙醇浓度74.934%、提取时间2.447h、液料比13.967:1,为了操作方便,选用乙醇浓度75%、提取时间2.5h、液料比14:1。进行响应面最优组合验证,得到三萜含量为(9.0713±0.01)mg/g、提取物得率为(3.10±0.02)%,与理论值9.0879mg/g、3.09%相比,相对误差较小,分别为0.18%和0.44%。
结合单因素结果可得优化的最佳工艺参数为:乙醇浓度75%、提取时间2.5h、液料比14:1,提取次数为2次。在此条件下进行实验室提取,得到的三萜含量为(10.6663± 0.0086)mg/g,提取物得率为(4.63±0.03)%。该结果均高于2.2.4中不同液料比提取两次的结果,说明采用单因素和响应面法优化得到的灵芝三萜加热回流提取的方法有效可行,可用于实际操作。
在该条件下进行中试放大提取,得到的三萜含量为11.8591mg/g,提取物得率为6.10%,与实验室验证结果相比,中试放大的三萜含量和提取物得率更高,可能是因为实验室回流是用加热套局部加热,而中试设备使用蒸汽夹套加热,热接触面积更大,因而提取更充分。
3 讨论
筛选出高三萜含量的灵芝子实体原料并有效提高三萜的提取率是灵芝产品开发的重要前提。灵芝中的三萜大都属于醇溶性成分,实验室内常用甲醇、乙醇、氯仿等有机溶剂提取。郑士彬等(2015)证实有机溶剂对灵芝三萜的提取效率依次为:氯仿>乙醇>甲醇,但在保健品生产中,考虑到产品的可食用性和安全性,只能选择乙醇作为提取溶剂。以往的研究中,单因素试验主要考察乙醇浓度、乙醇液料比、提取时间、提取次数(Oancea et al. 2012)等因素对三萜提取得率的影响,本研究则以三萜含量和提取物得率为综合考察指标。研究发现单因素对三萜含量和提取物得率的影响为:液料比>乙醇浓度>提取时间;且三萜含量和提取物得率受乙醇浓度和液料比交互作用的影响较大,受液料比和提取时间交互作用的影响不大;而乙醇浓度和提取时间对提取物得率的影响显著,对三萜含量的影响却并不显著。响应面优化的最佳工艺是在保证三萜含量与提取物得率均较高的前提下得到的,与仅用单一指标的优化试验相比结果更可靠,更有说服力。结合实际情况,确定的最优工艺参数为:乙醇浓度75%、提取时间2.5h、液料比14:1,提取次数2次。在此条件下,得到的三萜含量为(10.6663±0.0086)mg/g,提取物得率为(4.63±0.03)%;中试放大实验得到的三萜含量为11.8591mg/g,提取物得率为6.10%。优化的提取工艺可为灵芝三萜的规模化提取提供理论依据,为灵芝高附加值产品的开发利用奠定基础。
以往三萜含量的检测以化学法和液相色谱法为主。其中化学法由于显色剂对三萜类物质没有特异性,因而无法对某种特定三萜进行精确定量,且灵芝中含有较多的干扰物质(甾醇、脂肪酸等),导致三萜的测量值与实际值往往有较大的差异(张忠等 2016)。而液相色谱法利用三萜标准品进行定量分析,测量结果与化学法相比更为可靠,但由于部分灵芝三萜的保留时间相同,也会造成测定结果的不准确。超高效液相色谱-三重四级杆质谱联用技术(UPLC-MS/MS)在紫外检测的基础上添加质谱检测器,可根据保留时间和分子量信息对三萜进行分析,相比化学法和液相色谱法,可更加精确地检测三萜含量。本研究在UPLC-MS/MS分析方法的基础上,精确检测了7个栽培品种灵芝子实体原料中19个三萜化合物的含量,并筛选出三萜含量较高的sd-2灵芝子实体作为提取原料,比以往的分析结果更加精确可靠。
本研究使用液质联用技术对灵芝子实体中19个三萜化合物进行定量分析,虽然精确度高,结果更准确,但也存在一定的局限性。19个三萜化合物的保留时间都在32min之前,而灵芝sd-2子实体的超高效液相色谱图在32min之后仍有色谱峰出现,因此仅用19个三萜的含量代替灵芝总三萜含量进行判断也不够全面。这是由于灵芝子实体中三萜种类丰富、结构多样,除了本研究中19个含量较高的三萜酸类化合物外,灵芝子实体中还有很多含量较高、结构更复杂的灵芝醇、酮、醛类化合物,由于这些化合物不适合用ESI离子源进行分析而未被计算在内。因此,本研究获得的是灵芝酸类三萜的最佳提取工艺。
参考文献
Effects of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids on the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Species clarification of the prize medicinal Ganoderma mushroom “Lingzhi”
DOI:10.1007/s13225-012-0178-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Process optimization for biodiesel production from waste cooking palm oil (Elaeis guineensis) using response surface methodology
DOI:10.1021/ef8007954 URL [本文引用: 1]
Species diversity, taxonomy and phylogeny of Polyporaceae (Basidiomycota) in China
DOI:10.1007/s13225-019-00427-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
Comparison of two officinal Chinese pharmacopoeia species of Ganoderma based on chemical research with multiple technologies and chemometrics analysis
DOI:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.12.017 URL [本文引用: 1]
Notes on the nomenclature of the most widely cultivated Ganoderma species in China
Anti-tumor target prediction and activity verification of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids
Optimization of extraction and refining technology of Ganoderma lucidum total triterpenoids
Extraction, purification and preliminary structural analysis of triterpenoids from Ganoderma lucidum fermentation baking powder
Ganoderma triterpenoids exert antiatherogenic effects in mice by alleviating disturbed flow-Induced oxidative stress and inflammation
The study of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction for Ganoderma lucidum
DOI:10.1021/ie000203w URL
Study on the functional components in grass-cultivated Ganoderma lucidum and tree-cultivated Ganoderma lucidum
Determination of triterpenoids in Ganoderma lingzhi from different areas and varieties by HPLC
Determination of nine triterpenoid acids from Ganoderma lucidum of different producing areas by HPLC
Modern research on Ganoderma lucidum
4th ed.
The effects of ganoderma alcohols isolated from Ganoderma lucidum on the androgen receptor binding and the growth of LNCaP cells
DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2010.06.029 URL [本文引用: 1]
Triterpenoids of Ganoderma theaecolum and their hepatoprotective activities
DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2014.08.004
PMID:25111010
[本文引用: 1]

Five new lanostane triterpenoids, ganoderic acid XL1 (1), ganoderic acid XL2 (2), 20-hydroxy-ganoderic acid AM1 (3), ganoderenic acid AM1 (4) and ganoderesin C (5), together with five known triterpenoids (6-10) were isolated from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma theaecolum. Chemical structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic evidence, including 1D, 2D NMR, mass spectrometric data and circular dichroism spectra. Compounds 1, 4, 5, 8, 9 and 10 (10 μM) exhibited hepatoprotective activities against DL-galactosamine-induced cell damage in HL-7702 cells.Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Optimization of co-extraction of polysaccharides and triterpenoids from Ganoderma lingzhi by orthogonal design coupled with desirability and measurement of free radical scavenging activities of polysaccarides and triterpenoids extracted
Effects of extraction conditions on bioactive anthocyanin content of Vaccinium corymbosum in the perspective of food applications
DOI:10.1016/j.proeng.2012.07.440 URL [本文引用: 1]
Extraction of active triterpenoids in Ganoderma lucidum
Discovery of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids as potential inhibitors against Dengue virus NS2B-NS3 protease
DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-55723-5 URL [本文引用: 1]
Lanostane triterpenoids with anti- inflammatory activities from Ganoderma lucidum
DOI:10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.112256 URL [本文引用: 1]
Determination of total triterpenoids in fruiting body and spores of Ganoderma lucidum and assessment of their antitumor activity in vitro
A comparison of triterpenoids and polysaccharides in 13 species of wild Ganoderma
Resource diversity of Chinese macrofungi: edible, medicinal and poisonous species
DOI:10.1007/s13225-019-00432-7 URL [本文引用: 1]
Comparison study of triterpenoids from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma lucidum cultivated by difference strains
Discussion on the determination of total triterpenoids in Ganoderma lucidum by spectrophotometry
Study on the fingerprint and spectrum effect relationship of Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoid and the establishment of UPLC-MS/MS method
Optimization of refluxing extraction technology of triterpenoids from Ganoderma lucidum by response surface method
高效液相色谱法测定不同产地及品种灵芝三萜类成分的含量
13种野生灵芝菌丝体中胞内三萜与多糖含量的比较研究